Difference between revisions of "Me 410 B-6/R3"
(Detailed P&C is encouraged. Edited to reduce redundancy and number of bullet points) |
|||
| Line 301: | Line 301: | ||
* ''other literature.'' | * ''other literature.'' | ||
| + | {{AirManufacturer BFW}} | ||
{{Germany twin-engine fighters}} | {{Germany twin-engine fighters}} | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 30 December 2019
Contents
| This page is about the German twin-engine fighter Me 410 B-6/R3. For other uses, see Me 410 (Family). |
Description
The Me 410 B-6/R3 is a rank German twin-engine fighter
with a battle rating of (AB), (RB), and (SB). This aircraft has been in the game since the start of the Open Beta Test prior to Update 1.27.
General info
Flight Performance
Describe how the aircraft behaves in the air. Speed, manoeuvrability, acceleration and allowable loads - these are the most important characteristics of the vehicle.
| Characteristics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock | |||||||
| Max Speed (km/h at 6,900 m) |
Max altitude (meters) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (meters/second) |
Take-off run (meters) | |||
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | ||
| 598 | 582 | 32.2 | 33.2 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 520 | |
| Upgraded | |||||||
| Max Speed (km/h at 6,900 m) |
Max altitude (meters) | Turn time (seconds) | Rate of climb (meters/second) |
Take-off run (meters) | |||
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | ||
| 644 | 620 | 29.9 | 31.0 | 14.0 | 10.8 | 520 | |
Details
| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flap | Take-off flap | Landing flap | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X |
| Limits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wing-break speed (km/h) |
Gear limit (km/h) |
Combat flap (km/h) |
Max Static G | |
| + | - | |||
| 480 | ~9 | ~4 | ||
| Optimal velocities | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons (km/h) |
Rudder (km/h) |
Elevators (km/h) |
Radiator (km/h) |
| < 360 | < 360 | < 460 | > 265 |
| Compressor (RB/SB) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Setting 1 | ||
| Optimal altitude | 100% Engine power | WEP Engine power |
| 5,750 m | 3,120 hp | 3,551 hp |
Survivability and armour
- 8 mm steel - front of cockpit (either side of the glass)
- 5 mm steel - wings leading edge (in front of fuel tanks)
- 8 mm steel - prop hub and gear bay
- 9 mm steel - top and bottoms of wings (around the liquid cooling system
- 8 mm steel - plates in the tail
- 8 mm steel - bulkhead aft of gunner
- 8 mm steel - between gunner and pilot
- 12 mm steel - pilot's headrest
- 60 mm bulletproof glass - in front of the pilot (inside aircraft)
Armaments
Offensive armament
The Me 410 B-6/R3 is armed with:
- 2 x 30 mm MK 103 cannon, chin-mounted (120 rpg = 240 total)
- 2 x 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon, fuselage-mounted (350 rpg = 700 total)
Defensive armament
The Me 410 B-6/R3 is armed with:
- 1 x 13 mm MG 131 machine gun, 2 x beam turret (500 rpg = 1,000 total)
Usage in battles
The Me 410 B-6/R3, unlike its predecessors, has two 30 mm cannons in addition to the regular 20 mm cannons found on any Me 410. However, the 7.92 mm machine guns have been removed from the aircraft. With the 30 mm ammunition belts modification, the 30 mm cannons combined with HVAP-T belts make short work of light pillboxes, light and medium tanks, and even heavy tanks if hit on the side or back. Due to this, your primary goal should be unlocking the (Tier III) 30 mm ammunition belts.
The "Hornisse" is most well suited for bomber hunting due to its heavy armament. The aircraft can even use BnZ tactics against other aircraft, provided there is enough altitude. If you are planning to do aerial combat, be sure to side climb, as the 410's climb rate is far from superior to the Spitfires and Bearcats you will face. It is also equipped with airbrakes, which is quite unusual for an aircraft of its size and role. As with any plane, it is inadvisable to attack a bomber by sitting on its tail. It is advisable that you key-bind the 20 mm and 30 mm cannons separately if you are going for the CAS role it is well-suited for. Binding different buttons to fire the cannons separately can conserve a lot of ammo, as you can discriminate between which calibre to use when going after heavily-armoured or lightly-armoured targets. When choosing to go for the role of an interceptor, it is important (though you do not need too) that you cue the 30 mm and 20 mm together, as it will make much more of a difference in the 1-3 seconds worth of a good deflection.
Radars
The Me 410 B-6/R3 is equipped with a FuG 202 search radar, located in the nose of the aircraft; a control box which is part of the radar damage model is located behind the pilot.
| FuG 202 - Target Detection Radar | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Detection Range |
Guaranteed Detection Range |
Max Azimuth Scan Angle |
Max Elevation Scan Angle |
| 4,000 m | 4,000 m | ±30° | ±30° |
Manual Engine Control
| MEC elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixer | Pitch | Radiator | Supercharger | Turbocharger | ||
| Oil | Water | Type | ||||
| Not controllable | Controllable | Not controllable | Controllable | Combined | Not controllable | Not controllable |
Modules
| Tier | Flight performance | Survivability | Weaponry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Fuselage Repair | Radiator | Turret 13 mm | ||
| II | Compressor | Airframe | New 13 mm MGs (turret) | ||
| III | Wings Repair | Engine | Offensive 30 mm | Offensive 20 mm | |
| IV | Engine Injection | Cover | New 30 mm cannons | New 20 mm cannons | |
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Devastating high-velocity firepower with plentiful ammunition, is able to rip through any aircraft or vehicle in a short burst
- The defensive armament consists of two 13 mm machine guns, which can effectively chew through any aircraft's engine block
- Extremely versatile, can switch between CAP and CAS roles effectively
- The rear turrets have excellent coverage, covering almost all attacks from the rear of the aircraft
- Armour protects vital areas, such as the tail gunner, radiators, engines, and leading edges of the wing
- Has access to a target detection radar
- Is equipped with airbrakes, allowing for tighter turns and steeper dive angles
- Accelerates quite fast, especially in level flight
- Engine power is sufficient that it can fly on one engine
- Engines will cool down slowly even when the throttle is 100%
- Does not lose a significant amount of energy during manoeuvres
- Low-speed manoeuvring is impressive for the plane type due to slats
- Starts flying in a match with an air spawn
Cons:
- Large target
- Limited pilot protection, the pilot's torso and chest areas are not protected by armour
- Rate of climb is impairing
- Enters compressibility all too often when reaching 350 mph (563 km/h)
- Lacks effective ground attack without 30 mm HVAP
- No payload options
- Below mediocre maneuverabilty, especially roll rate, when compared to its rivals
- Tends to pitch up when extending flaps, can be deadly while landing
History
Describe the history of the creation and combat usage of the aircraft in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too big, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the vehicle and adding a block "/ History" (example: https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Vehicle-name)/History) and add a link to it here using the main template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <ref>, as well as adding them at the end of the article. This section may also include the vehicle's dev blog entry (if applicable) and the in-game encyclopedia description (under === Encyclopedia Info ===, also if applicable).
In-game description
"In addition to the main Me.410B modifications, a number of special-purpose variants of the Hornet were created for maritime operations. The anti-ship Me.410B-6/R3 modification was equipped with a FuG 200 Hohentwiel patrol radar system and a suspended WB 103 container with two 30 mm Rheinmetall-Borsig MK 103 cannons.
Also, several Me.410B-2/U3 planes received a FuG 200 radar, with the nose-mounted 13 mm Rheinmetall-Borsig MG 13 machine guns removed.
The Me.410B-5 maritime attack aircraft, with glide bombs (BT-Körper) as its main weapon, was to become the most significant Me.410 variation for sea operations. The bombs could only be suspended externally: two 400 kg BT 400s under the fuselage or up to six 200 kg BT 200s (two bombs under the fuselage and four under the wings). The aircraft was equipped with a FuG 200 radar and two 20 mm Mauser MG 151/20 cannons. The 13 mm Rheinmetall-Borsig MG 131 machine guns, both in the nose section and in the remote-controlled FDL 131 mobile mounts, were removed. The bomb bay was not used as a bomb bay and instead had an extra 650-litre fuel tank mounted inside. Instead of BT bombs, the Me.410B-5 could carry a 900 kg LT5b aerial torpedo, a 760 kg LT5i, or a 1,800 kg SC 1800 bomb. When a SC 1800 was included, the fuel tank was removed from the bomb bay.
Other types of anti-ship weapons were also tested on the Me.410B-5, such as the 800 kg SB 800RS bouncing bomb or the 1,000 kg SB 1000/400 bomb, with a decreased diameter designed to reduce drag. The bomb was stabilized by a braking parachute upon its being dropped.
In May 1943, the first Me.410s appeared in the front line in Tunisia. In June 1943, the Hornets took part in raids over Britain. Beginning in April 1944, they were used by the German Air Defence Force.
Although the Me.410 was superior to the Bf 110 in its performance characteristics, most of all in its speed and flight range, it was inferior as far as versatility was concerned. The Me.410's production was discontinued in September 1944. By this time, 1,160 machines were built in all versions, including bombers and scouts. It should be noted that some aircraft were redesigned Me.210s whose construction had not yet been completed."
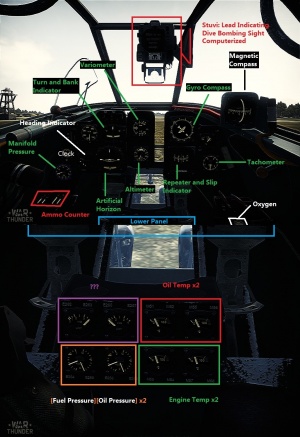
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the aircraft;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:
- topic on the official game forum;
- encyclopedia page on the aircraft;
- other literature.
| Germany twin-engine fighters | |
|---|---|
| Messerschmitt | Bf 109 Z-1 |
| Me 410 A-1/U2 · Me 410 B-1/U2 | |
| Dornier | Do 17 Z-7 · Do 217 J-1 · Do 217 J-2 · Do 217 N-1 · Do 217 N-2 |
| Focke-Wulf | Ta 154 A-1 |
| Junkers | Ju 88 C-6 · Ju 388 J |