Difference between revisions of "T-34-100"
(Edits) |
(→Ammo racks: Corrected error) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
! Visual<br>discrepancy | ! Visual<br>discrepancy | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | '''30''' || 29 ''(+1)'' || 27 ''(+3)'' || 25 ''(+25)'' || 10 ''(+20)'' || | + | | '''30''' || 29 ''(+1)'' || 27 ''(+3)'' || 25 ''(+25)'' || 10 ''(+20)'' || 4 ''(+26)'' || 1 ''(+29)'' || No |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 23:28, 11 March 2023
| This page is about the Soviet medium tank T-34-100. For other variants, see T-34 (Family). |
Contents
Description
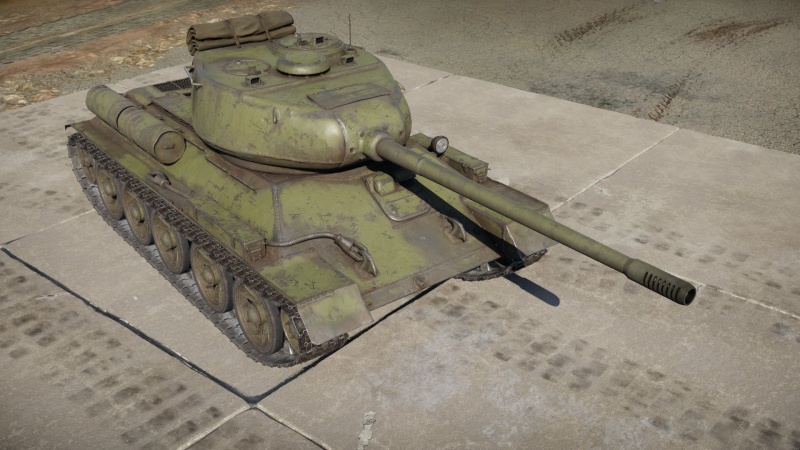
The T-34-100 is a premium rank Soviet medium tank with a battle rating of (AB), (RB), and (SB). It was introduced in Update 1.51 "Cold Steel". The vehicle is that of a T-34 hull and chassis, but with a heavy emphasis in firepower with a 100 mm LB-1 gun as its main armament. This gun is equivalent to those on the SU-100 and the T-54 series. Thus, while suffering from a now obsolete armour thickness, it has the firepower needed to compete on an SF-SF - "see first, shoot first" basis.
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour (Hull, Turret roof)
- Cast homogeneous armour (Turret, Driver's hatch)
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 45 mm (60°) Front glacis 45 mm (55°) Lower glacis 75 mm (60°) Driver's hatch |
45 mm (40-41°) Top 45 mm Bottom |
45 mm (48-50°) Top 45 mm (48°) Bottom |
20 mm |
| Turret | 90 mm (2-65°) Turret front 90 mm (3-69°) Gun mantlet |
75 mm (15-16°) Front 2/3rd 52 mm (10-11°) Rear 1/3rd |
52 mm (11-13°) | 20 mm |
| Cupola | 90 mm | 90 mm | 90 mm | 20 mm |
Notes:
- Suspensions wheels and tracks are 20 mm thick.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | Expression error: Unexpected * operator. | 775 | Expression error: Unexpected round operator. | __.__ | |||
| Realistic | 442 | Expression error: Unexpected round operator. | __.__ | ||||
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
| 100 mm LB-1 | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 30 | -3°/+18° | ±180° | N/A | 23.80 | 32.94 | 40.00 | 44.24 | 47.06 | 14.95 | 13.23 | 12.19 | 11.50 |
| Realistic | 14.88 | 17.50 | 21.25 | 23.50 | 25.00 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| BR-412 | APHE | 218 | 212 | 189 | 164 | 142 | 124 |
| BR-412B | APHEBC | 218 | 215 | 201 | 184 | 169 | 155 |
| BR-412D | APCBC | 239 | 236 | 220 | 202 | 185 | 170 |
| OF-412 | HE | 27 | 27 | 26 | 24 | 23 | 21 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | |||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| BR-412 | APHE | 895 | 15.88 | 1.2 | 19 | 100.1 | 47° | 60° | 65° | |||
| BR-412B | APHEBC | 895 | 15.88 | 1.2 | 19 | 100.1 | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| BR-412D | APCBC | 887 | 15.88 | 1.2 | 19 | 100.1 | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| OF-412 | HE | 900 | 15.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1,460 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |||
| Smoke shell characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Screen radius (m) |
Screen deploy time (s) |
Screen hold time (s) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
| 3D3 | 880 | 15.6 | 16 | 5 | 25 | 50 |
Ammo racks
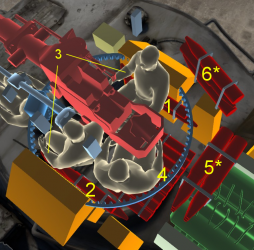
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
6th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 29 (+1) | 27 (+3) | 25 (+25) | 10 (+20) | 4 (+26) | 1 (+29) | No |
Notes:
- Shells are modeled individually and disappear after having been shot or loaded.
- Racks 5 and 6 are first stage ammo racks. They total 9 shells and get filled first when loading up the tank.
- These racks are also emptied early: the rack depletion order at full capacity is: 6 - 5 - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4.
- Simply not firing when the gun is loaded will move ammo from racks 1-4 into rack 5 then 6. Firing will interrupt the restocking of the ready rack.
- Hull empty: 10 (+20) shells.
Machine guns
| 7.62 mm DT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaxial | 1,890 (63) | 600 | N/A | N/A |
Usage in battles
The T-34-100 retains the mobility, agility, and armour of the T-34-85 and combines it with a much more powerful gun only seen on tank destroyers in the same rank. However, its overall performance is limited by the fact that its armour is essentially paper-thin against the kind of guns the enemies can field at this rank.
These characteristics mean the T-34-100 excels as either an assaulter or a flanker.
- Assaulter
Make use of the T-34-100's mobility and move towards the objective. Make sure that the T-34-100 is advancing with teammates, as if the T-34-100 encounters an enemy first, the enemy's guns will make short work of the T-34-100's armour. Ideally, allow a more heavily armoured teammate to take in the enemy's attention. While the enemy is focused on the ally, move to an ideal firing position to attack the enemies with the 100 mm gun. If an opening presents itself to the T-34-100, charge into the objective and begin capturing it while in cover. Once captured, move on to the next point or stay in the captured point as a defender to attack enemies attempting to roll in by popping out and taking a shot.
- Flanker
The T-34-100 on large map can utilise its mobility to go around the outskirts of the map to show up in unexpected locations on the sides or behind the enemy. Find a cover to hide the tank behind, then pop out and shoot an unsuspecting enemy before withdrawing back to safety. Due to the gun's terrible depression angles, the ideal terrain for a firing position is a flat piece of land. This means that any attempt to take a shot against the enemy is likely to expose a large portion of the T-34-100's armour, from which the enemy can shoot and quickly cripple or destroy the T-34-100. As such, after every shot, withdraw back into cover to preserve the T-34-100's lifespan.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Excellent speed and agility
- Powerful 100 mm gun
- Rear-mounted transmission
Cons:
- Higher profile than other T-34s due to larger turret
- Bad gun depression
- Armour is extremely poor
History
The T-34
Issued in large numbers in 1940, the T-34 became largely known as one of the best medium tanks of World War II. At its introduction, there was nothing comparable in any other army in the World, the Germans were still with their Panzer IIIs and Panzer IVs while the Americans had access to their inter-war period M2 medium tank and M3 Stuart light tanks. The T-34 featured a frontal armour plate of 45 mm thick but sloped at 60 degrees to create a 90 mm effective armour, a lot more than its contemporaries. The addition of a 76.2 mm gun also gave the T-34 a much better firepower advantage than other tanks as well. Its superiority in armour, mobility, and firepower caught the Germans by surprise when Operation Barbarossa was launched, and they found that many of their anti-tank weapons available were unable to destroy the T-34. However, poor unit coordination and crew training with the T-34 gave them little opportunities to be used in the most efficient way possible against the Germans.
By 1943, however, with the T-34 shock over in Germany, they had been developing better anti-tank weapons to fight back the T-34 such as the high-velocity Pak 40 anti-tank gun. They also upgraded their current tank arsenal with better guns, such as giving the Panzer IV a 7.5 cm KwK40 L43 cannon that could penetrate the T-34. Not only that, the introduction of heavier, more armoured tanks such as the Panthers and Tigers with much better guns could not only take out the T-34 at long ranges, but are also immune to the 76.2 mm gun from anywhere except in really close ranges or onto the sides. This lack in firepower the T-34 experienced made the Soviet High Command advocate for an upgrade in the T-34, and after adapting an aircraft gun and a turret from a cancelled project, it was called the T-34-85, which had a 85 mm gun. The upgraded gun gave the T-34 a much-needed boost in firepower that it lacked in the later part of World War II, and this model became the standard T-34 until the end of the war.
Development
In 1944, it was widely believed that the T-34-85 was still inferior to German tanks such as the Panther and attempts were made to up-gun the tank. First was the attempt by Factory No.192 to mount a higher powered 85 mm gun (dubbed the ZiS-85-BM) onto the T-34 in September 1944, but this proved a failure in trials. The second was in October 1944 where Factory "Bolshevik" develop another high-powered 85 mm gun called V-5 and V-9K, but this also proved a failure when it is unable to keep with the 88 mm KwK43 gun on the Tiger II. This development then proceeded more ambitiously to a bigger gun. It was decided that the gun would be a 100 mm calibre and the task for this adaption fell to Plant No. 9 and No. 183 in July 1944. But findings say that the turret ring on the T-34-85 was not enough to mount the 100 mm cannon, and attempting to enlarge the turret ring for the IS-2 turret to 1,800 mm was impossible. It fell to A. Savinov from Factory No.92 to adapt the 100 mm gun onto the T-34-85's turret, but trials found that this improvisation was not successful due to the excessive weight of the gun.
The design bureaus continued their research, now working alongside the development of the T-44 tank. A solution was to create a somewhat "hybrid" of a vehicle between the T-34 and the T-44, which resulted in a larger turret ring of 1,700 mm and other changes to the T-34 suspension to make it more durable. The turret could hold the 100 mm cannon and all the modifications made the vehicle weigh about 33 tons. This vehicle was designated the T-34-100. Trials with this gun in early 1945 using both the 100 mm ZiS-100 and the D-10T (from the SU-100) showed that the vehicle was relatively successful, even if accuracy was not the best and that the gun put a strain onto the suspensions when fired. However, the Red Army like this vehicle and pushed for further development to eliminate most of the flaws the tank is associated with.
At the end of 1944, a newer 100 mm gun called the LB-1 was developed that had less recoil than the ZiS-100 and was proposed to be mounted onto the T-34 as well to eliminate the flaws the gun is doing onto the tank. But the gun was very long, extending 3 m farther than the tank dimension itself. The T-34-100 mounting the LB-1 was tested in April 1945, firing tests and driving tests were conducted and it was found that the 100 mm LB-1 was much more accurate than its predecessors and did not affect the tank suspension as much. With a practical rate of fire of 5 rounds a minute, the rate of fire for the calibre was a lot higher and gave the tank a much better firepower advantage when used. However, as successful the trials were, the T-34-100 never entered full production as World War II was coming to an end, with the Red Army already encircling Berlin as these tests were made. Plus, the development of newer tanks such as the T-44 would give the Red Army a new platform of upgrade flexibility, rather than continuing to use a pre-war design made in 1940.
The 100 mm will live on in the T-54, a tank derived from the T-44 tank, and it would become the most numerous tank design in the world.
| Archive of the in-game description | |
|---|---|
|
The T-34-100 medium tank was the last attempt to enhance the tank's firepower while preserving its primary dynamic characteristics. Once the T-34-85 modification was armed it became clear that the T-34-85 could successfully go up against German heavy tanks when firing from an ambush or at close range, which had not always been possible. OKB #9 Factory #183 received the order to install a 100 mm gun on the standard T-34-85 turret. Once they had begun drafting the project, the engineers quickly came to the conclusion that doing this while preserving the turret's previous 1,600 mm drive was impossible. A test stand was built at the factory consisting of the power train and body of a T-34-85 and the turret of the experimental T-44 tank. Given that the turret's drive was 1,700, the body still had to be rebuilt. In order to reduce the tank's weight, the bow gun was removed, and the crew compliment was reduced by one. After all these modifications were complete the tank received the designation T-34-100. | |
Media
- Skins
- Videos
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
| Kharkov Design Bureau for Mechanical Engineering named after A. A. Morozov | |
|---|---|
| Light Tanks | |
| BT-5 | BT-5 · RBT-5 |
| BT-7 | BT-7 · BT-7M · BT-7A (F-32) |
| Medium Tanks | |
| T-34-76 | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1940) · T-34 (1941) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34 (1942) · T-34E STZ · T-34E |
| T-34-57 | T-34-57 · T-34-57 (1943) |
| T-34-85 | T-34-85 (D-5T) · T-34-85 · T-34-85E |
| T-34-100 | T-34-100 |
| T-44 | T-44 · T-44-100 · T-44-122 |
| Main Battle Tanks | |
| T-54 | T-54 (1947) · T-54 (1949) · T-54 (1951) |
| T-64 | T-64A (1971) · T-64B |
| Export/Captured | |
| T-34 | ▀T 34 747 (r) · ▄T-34 · ▄T-34-85 · ␗T-34 (1943) · ␗Т-34-85 (S-53) |
| T-54 | ▄T-54 |
| See Also | Uralmashzavod · Uralvagonzavod |
| USSR medium tanks | |
|---|---|
| T-28 | T-28 (1938) · T-28 · T-28E |
| T-34-76 | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1940) · T-34 (1941) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34 (1942) · T-34E STZ · T-34E |
| T-34-57 | T-34-57 · T-34-57 (1943) |
| T-34-85 | T-34-85 (D-5T) · T-34-85 · T-34-85E |
| T-34-100 | T-34-100 |
| T-44 | T-44 · T-44-100 · T-44-122 |
| T-54 | T-54 (1947) · T-54 (1949) · T-54 (1951) |
| T-55 | TO-55 · T-55A · T-55AM-1 · T-55AMD-1 |
| T-62 | T-62 · T-62M-1 |
| T-64 | Object 435 · T-64A (1971) · T-64B |
| T-72 | T-72A · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-72B · T-72B (1989) · T-72B3 · T-72M2 Moderna |
| T-80 | T-80B · T-80U · T-80UD · T-80UK · T-80UM2 · Т-80U-Е1 · T-80BVM · Object 292 |
| T-90 | Т-90А · T-90M |
| Trophies/Lend-Lease | |
| Germany | ▂T-III · ▂T-V |
| Great Britain | ▂МК-IX "Valentine" |
| USA | ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 |
| USSR premium ground vehicles | |
|---|---|
| Light tanks | BA-11 · RBT-5 · BT-7A (F-32) · T-26 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-26E · T-126 · PT-76-57 · 2S38 |
| Medium tanks | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34E · T-34-57 (1943) · T-34-85E · T-34-100 · T-44-122 · TO-55 · T-55AM-1 · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-80UD · Т-80U-Е1 |
| ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 · ▂T-III · ▂T-V · ▂МК-IX "Valentine" | |
| Heavy tanks | SMK · T-35 · ▂MK-II "Matilda" · KV-1E · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) · KV-122 · KV-220 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 · IS-6 · T-10A |
| Tank destroyers | BM-8-24 · BM-13N · BM-31-12 |
| SU-57 · SU-76D · SU-76M (5th Gv.Kav.Corps) · SU-85A · SU-100Y · SU-122P · Object 120 | |
| SPAA | ▂Phòng không T-34 · ZUT-37 |





