Difference between revisions of "B-24D-25-CO"
(Updated page template) |
(→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
* Significantly lower payload compared to heavy bombers of other nations | * Significantly lower payload compared to heavy bombers of other nations | ||
* Twin tail configuration reduces manoeuvrability, rectified in [[PB4Y-2|PB4Y-2 ''Privateer'']] with a single tail | * Twin tail configuration reduces manoeuvrability, rectified in [[PB4Y-2|PB4Y-2 ''Privateer'']] with a single tail | ||
| + | * At a bad BR for AB/RB and will likely be shot down before a successful bombing run | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 237: | Line 238: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''reference to the series of the aircraft;'' | * ''reference to the series of the aircraft;'' | ||
* ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' | * ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' | ||
| Line 242: | Line 244: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
* ''encyclopedia page on the aircraft;'' | * ''encyclopedia page on the aircraft;'' | ||
Revision as of 09:58, 16 August 2020
Contents
| This page is about the American heavy bomber B-24D-25-CO Liberator. For other versions, see B-24/PB4Y (Family). |
Description
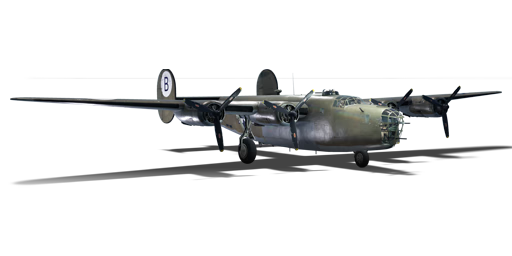
The B-24D-25-CO Liberator is a rank American bomber
with a battle rating of (AB), (RB), and (SB). It has been in the game since the start of the Open Beta Test prior to Update 1.27.
The Consolidated B-24D Liberator was built to be a long-range four-engine heavy bomber. It is most efficiently used for bombing stationary targets like bases, airfields, and pillboxes from high altitude.
The Liberator can cruise somewhat faster than the Boeing B-17E Flying Fortress and can also carry a heavier payload. Unfortunately, its manoeuvrability and handling are significantly worse thanks to the Davis wing design, which is optimized for efficient level flight only. Evasive manoeuvres are not easy to pull off and typically result in loss of altitude or going into a spin.
In line with the USAAF's philosophy during World War II, the Liberator is equipped with a relatively heavy defensive armament of eleven .50 cal AN/M2 heavy machine guns staffed by gunners. The theory behind this was intended that an American bomber would be able to defend itself from enemy fighters in daylight missions. These guns have excellent coverage and there is no angle from which attackers may come from on which no guns can be brought to bear.
Compared to the B-17E, the Liberator can carry an additional 2 x 1,000 lb (454 kg) bombs. However, this maximum payload of 8,000 lb (3,632 kg) compares very unfavourably against other heavy bombers like the Yermolayev Yer-2 with ACh-30B engines (5,000 kg), Dornier Do 217 series (4,000 kg), and Lancaster series (14,000 lb or 6,363 kg), all of which have much lower battle ratings. On the flip side, while its payload may not have been as great as other nation's bombers, over 18,500 B-24 bombers were built over the duration of the war (the most produced bomber) and were deployed in sheer numbers unmatched by any other bomber.
General info
Flight performance
Describe how the aircraft behaves in the air. Speed, manoeuvrability, acceleration and allowable loads - these are the most important characteristics of the vehicle.
| Characteristics | Max Speed (km/h at 7,620 m) |
Max altitude (metres) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (metres/second) |
Take-off run (metres) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||
| Stock | 477 | 465 | 39.1 | 40.2 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 820 | |
| Upgraded | ___ | ___ | __._ | __._ | __._ | __._ | ||
Details
| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| X | ✓ | ✓ | X | X |
| Limits | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wings (km/h) | Gear (km/h) | Flaps (km/h) | Max Static G | |||
| Combat | Take-off | Landing | + | - | ||
| N/A | 390 | 263 | ~3 | ~1 | ||
| Optimal velocities (km/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons | Rudder | Elevators | Radiator |
| < 200 | < 180 | < 180 | > 300 |
| Compressor (RB/SB) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Setting 1 | ||
| Optimal altitude | 100% Engine power | WEP Engine power |
| 6,620 m | 4,400 hp | 4,752 hp |
Survivability and armour
- 9.5 mm Steel - Armour plates behind the pilots
- 9.5 mm Steel - Armour plates in front of the dorsal gunner
- 9.5 mm Steel - Armour plate in front of the ventral gunner
- 9.5 mm Steel - Armour plate behind beam gunners
- 9.5 mm Steel - Armour plates around the tail gunner
- 38 mm Bulletproof glass - Tail gunner's rear facing window
Armaments
Suspended armament
The B-24D-25-CO can be outfitted with the following ordnance:
- 8 x 500 lb AN-M64A1 bombs (4,000 lb total)
- 20 x 100 lb AN-M30A1 bombs (2,000 lb total)
- 12 x 500 lb AN-M64A1 bombs (6,000 lb total)
- 8 x 1,000 lb AN-M65A1 bombs (8,000 lb total)
Defensive armament
The B-24D-25-CO is defended by:
- 3 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine gun, nose turret (300 rpg = 900 total)
- 2 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns, dorsal turret (200 rpg = 400 total)
- 2 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns, ventral turret (275 rpg = 550 total)
- 1 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine gun, 2 x beam turret (250 rpg)
- 2 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns, tail turret (400 rpg = 800 total)
Usage in battles
Due to its high battle rating, the Liberator will face many high-altitude dedicated bomber interceptors with 20–30 mm cannons, making for an extremely dangerous environment. The defensive guns should be treated as a last resort; combat with fighters should be avoided at all costs by the use of careful route planning and cloud cover, if available.
If pursued, attempt to manoeuvre the Liberator so that the enemy is forced into a tail-chase, where the Liberator's defensive guns are most effective.
Low-level bombing is not recommended due to the limited manoeuvrability of the aircraft, the Liberator simply doesn't have the performance to get away with it and you will be an easy target for enemy fighters.
Counter-tactics
When going up against the B-24D, it is very important that the attacker must never underestimate the sheer defensive power this bomber holds. If not careful, your plane will either become critically damaged or a ball of fire from only a few hits from the 12.7 mm M2 Browning MGs.
The number one rule when fighting a bomber is to never engage it in front or the back; this applies heavily when engaging the B-24D since you will have 6 machine guns facing you. The best way to attack this bomber is from above or the sides. Attacking from below is highly discouraged since you will be forced to pull up in order to engage and end up above the bomber where 4 machine guns will be facing you automatically. Boom & Zoom tactics are highly recommended since it allows you to evade machine gun fire and be on the constant move at high speeds making it difficult for the gunners to get a bead on you.
When engaging the B-24D, you must always keep your momentum and never stall or bleed your speed. Losing speed means you are an easier target to hit, which means you are an easier target to shoot down. Aiming at the engines will also stress your opponent as it will cause the bomber to lose speed rapidly or even better, catch fire. If you wish for an easy kill without wasting precious time, it is recommended to aim for the bomber's wings. Damaging the wings of the plane will cause it to tilt to one side or snap.
The last thing a player should take note is the plane they plane they are flying. As bad as it sounds, a Japanese plane is more likely to be brought down than a German plane due to the difference in armour, it is better to bring an aircraft with some form of protection rather than a plane with no protection, this will determine your chances of survival by a great amount.
Manual Engine Control
| MEC elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixer | Pitch | Radiator | Supercharger | Turbocharger | ||
| Oil | Water | Type | ||||
| Controllable | Controllable Auto control available |
Not controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Not auto controlled |
Combined | Controllable 1 gear |
Auto controlled |
Modules
| Tier | Flight performance | Survivability | Weaponry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Fuselage repair | Radiator | Protective vest | SBC-24 | Turret 12 mm |
| II | Compressor | Airframe | New 12 mm MGs (turret) | ||
| III | Wings repair | Engine | MBC-24 | ||
| IV | Engine injection | Cover | LBC-24 | ||
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Heavy defensive armament, protected from every angle (deadly from frontal and rear attacks)
- Heavier payload than the B-17E, however comparable to B-17G
- Overall better flight performance than the B-17E in level flight
Cons:
- Poor handling, built for top speed a level flight, not manoeuvring
- Significantly lower payload compared to heavy bombers of other nations
- Twin tail configuration reduces manoeuvrability, rectified in PB4Y-2 Privateer with a single tail
- At a bad BR for AB/RB and will likely be shot down before a successful bombing run
History
The B-24 was produced in several variants to fulfil operational and training needs. More Liberators were eventually built than any other US Warplane during World War II. The first B-24 prototype flew in December of 1943 named "XB-24". The aircraft was designed around the "Davis" wing, a long, thin, large area structure mounted high on the fuselage. The long wingspan gave the B-24 excellent high altitude performance and allowed it to extend its range. The twin bomb-bays were called "roller shutter" doors. The doors rolled up into the aircraft. The purpose of this design was to reduce the drag while the bomb bay doors are open. The bomb-load was stored vertically with a catwalk down the middle, this gave crews easy access to the rear of the fuselage. The Liberator was powered by four 1,200 HP Pratt & Whitney R-1830 engines. The aircraft also included a twin tail design and tricycle landing gear.
The B-24 made its operational debut in June of 1942. It was tasked with long-range raids on Germany's Romanian oilfields. The B-24 is commonly remembered for its service with the Eighth Air Force but it filled a desperate roll for the navy as a long-range patrol aircraft. After huge losses of allied shipping, the Navy was granted access to Liberators. These aircraft were operated under the designation PB4Y. They were equipped with air to surface radar and depth charges. The B-24 also quickly replaced the B-17 in the Pacific theatre due to its long-range capabilities. The B-24 was used to bring havoc to Japanese land installations and naval vessels. Liberators stayed in service until 1951, they were replaced by the Privateer.
The B-24 is often unfairly compared to the B-17. The B-24 was newer, more efficient, and much more versatile then Boeing's design. The B-24 saw action on all fronts, its most valuable work may have been against U-boats. The aircraft also saw work as a cargo plane, tanker, patrol, and reconnaissance. Even some were armed with additional guns as escorts. The B-24 was not as popular with its crews as the B-17. The B-24 was known to catch fire in battle easier and at times was known to suffer from hydraulic problems.
In-game description
The Consolidated B-24D "Liberator" heavy bomber was created as a part of "Project A" a program launched to enhance the USA's industrial capacity to meet the needs of the Air Force. The contract for the aircraft, which was to be an improved B-17, was received by Consolidated in March of 1939, with a prototype required by the end of the year. The prototype was finished and made its first flight just two days before the deadline on December 29.
The new aircraft, although more difficult to control, was superior to the B-17 in range, operational ceiling, and maximum speed. In addition, it could carry a significantly larger bomb load (up to 3629 kg), which largely determined its application: the first models delivered to England were mainly used for coastal protection from German submarines.
The first successful modification of the aircraft was the B-24D, which was mass-produced from 1940 to 1942. This model had four 1200 hp engines, and its armament was modified over time, based on pilot feedback. Eventually, it was equipped with eleven 12.7mm machine guns (three in the nose, two remote-controlled guns in the dorsal turret, two in the ventral ball turret, one machine gun in each side window, and two machine guns in the tail turret).
The B-24 was the most mass-produced Allied bomber in World War II - all in all, 18,482 B-24s were produced, 2,696 of which were B-24Ds. These bombers were made in several factories. The factory which produced the most was the Henry Ford plant in Willow Run, which in 1944 released a B-24 every hour, 650 planes per month.
The B-24 was actively used in the Pacific and European theaters of war.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the aircraft;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:
- topic on the official game forum;
- encyclopedia page on the aircraft;
- other literature.
| Consolidated Aircraft Corporation | |
|---|---|
| Bombers | PBY-5 Catalina · PBY-5A Catalina |
| PB4Y-2 | |
| B-24D-25-CO | |
| Export | ▄Catalina Mk IIIa · ▂PBY-5A Catalina · ▄PBY-5A Late · ␗PB4Y-2 · ▄PB4Y-2 |
| USA bombers | |
|---|---|
| Dive | SB2U-2 · SB2U-3 · SBD-3 · SB2C-1C · SB2C-4 |
| Torpedo | TBD-1 · PBY-5 Catalina · PBY-5A Catalina · TBF-1C · BTD-1 |
| Medium | B-10B · B-18A · B-34 · PV-2D · B-25J-1 · B-25J-20 · A-26C-45 · A-26C-45DT · B-26B |
| Heavy | B-17E · B-17E/L · B-17G-60-VE · PB4Y-2 · B-24D-25-CO · B-29A-BN |
| Hydroplanes | OS2U-1 · OS2U-3 · PBM-1 "Mariner" · PBM-3 "Mariner" · PBM-5A "Mariner" |