Difference between revisions of "IS-4M"
(Restored page, Updated template w/ new design) |
(→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
''If necessary use a visual template to indicate the most secure and weak zones of the armour.''--> | ''If necessary use a visual template to indicate the most secure and weak zones of the armour.''--> | ||
'''Armour type:''' | '''Armour type:''' | ||
| + | |||
* Rolled homogeneous armour (Hull, Turret roof, Hatch roof) | * Rolled homogeneous armour (Hull, Turret roof, Hatch roof) | ||
* Cast homogeneous armour (Turret) | * Cast homogeneous armour (Turret) | ||
| + | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Notes:''' | '''Notes:''' | ||
| + | |||
* Suspension wheels are 20 mm thick, torsion bars are 10 mm thick, and tracks are 30 mm thick. | * Suspension wheels are 20 mm thick, torsion bars are 10 mm thick, and tracks are 30 mm thick. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 34: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="3" | Mobility characteristic | + | ! colspan="3" | Mobility characteristic |
|- | |- | ||
! Weight (tons) | ! Weight (tons) | ||
| − | !colspan="1" | Add-on Armour<br>weight (tons) | + | ! colspan="1" | Add-on Armour<br>weight (tons) |
| − | !colspan="1" | Max speed (km/h) | + | ! colspan="1" | Max speed (km/h) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |rowspan="2" | 60.0 || colspan="1" rowspan="2" | N/A || colspan="1" | 45 (AB) | + | | rowspan="2" | 60.0 || colspan="1" rowspan="2" | N/A || colspan="1" | 45 (AB) |
|- | |- | ||
|43 (RB/SB) | |43 (RB/SB) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="3" | Engine power (horsepower) | + | ! colspan="3" | Engine power (horsepower) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="1" | Mode | + | ! colspan="1" | Mode |
!Stock | !Stock | ||
!Upgraded | !Upgraded | ||
| Line 55: | Line 58: | ||
|750 | |750 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="3" | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | + | ! colspan="3" | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | !colspan="1" | Mode | + | ! colspan="1" | Mode |
!Stock | !Stock | ||
!Upgraded | !Upgraded | ||
| Line 169: | Line 172: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! class="wikitable unsortable" |Full<br /> ammo | ! class="wikitable unsortable" |Full<br /> ammo | ||
| − | ! class="wikitable unsortable" |Ammo<br/>Part | + | ! class="wikitable unsortable" |Ammo<br />Part |
! class="wikitable unsortable" |1st<br /> rack empty | ! class="wikitable unsortable" |1st<br /> rack empty | ||
! class="wikitable unsortable" |2nd<br /> rack empty | ! class="wikitable unsortable" |2nd<br /> rack empty | ||
| Line 218: | Line 221: | ||
'''Pros:''' | '''Pros:''' | ||
| − | * Very good frontal armour; can | + | * Very good frontal armour; can even bounce 128 mm shells from the Maus. |
* Retains the powerful D-25T 122mm gun as on the previous IS-2 and IS-3 | * Retains the powerful D-25T 122mm gun as on the previous IS-2 and IS-3 | ||
| + | * The mere presence of an IS-4 can make enemies panic or run and hide. | ||
| + | * Slightly wider choices of ammo compared to the IS-2 and IS-3. | ||
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| Line 225: | Line 230: | ||
* Can - and will - be a priority target for the enemy team due to its fearsome reputation | * Can - and will - be a priority target for the enemy team due to its fearsome reputation | ||
* Long reload of 20 seconds | * Long reload of 20 seconds | ||
| + | * Ammo rack in back of the turret; if a shell penetrates, the ammo could detonate. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 232: | Line 238: | ||
===Usage=== | ===Usage=== | ||
| − | ''Object 701'' was eventually approved for production in 1947 as the '''IS-4'''. The production turned out 200 tanks (some sources say 250) before the production was halted. The reason being that the IS-4 was criticized for being inadequate in mobility despite its new engine.<ref name="ZalogaIS"/> While production ended, the remaining IS-4 still saw service in the Soviet Union. When the Korean War broke out in 1950 and the United States and its allies got involved, the IS-4s were all shipped to the Far East of the Soviet Union in anticipation of Soviet intervention in the Korean War. They were not committed despite pressure by the Chinese from fear of inciting another world war. Even so, the IS-4 stayed in the region ready for action. In the late 1950s, the IS-4 underwent a modernization program along the lines of the IS-3 with increased ammo stowage, new machine gun armaments, new gun optics, better engine, and better filtration system and this modernized variant was named the '''IS-4M'''.<ref name="ZalogaIS"/> The IS-4 stayed in service in the Soviet Union until the 1960s. | + | ''Object 701'' was eventually approved for production in 1947 as the '''IS-4'''. The production turned out 200 tanks (some sources say 250) before the production was halted. The reason being that the IS-4 was criticized for being inadequate in mobility despite its new engine.<ref name="ZalogaIS" /> While production ended, the remaining IS-4 still saw service in the Soviet Union. When the Korean War broke out in 1950 and the United States and its allies got involved, the IS-4s were all shipped to the Far East of the Soviet Union in anticipation of Soviet intervention in the Korean War. They were not committed despite pressure by the Chinese from fear of inciting another world war. Even so, the IS-4 stayed in the region ready for action. In the late 1950s, the IS-4 underwent a modernization program along the lines of the IS-3 with increased ammo stowage, new machine gun armaments, new gun optics, better engine, and better filtration system and this modernized variant was named the '''IS-4M'''.<ref name="ZalogaIS" /> The IS-4 stayed in service in the Soviet Union until the 1960s. |
===Legacy=== | ===Legacy=== | ||
| − | The IS-4, as a relatively unsuccessful Soviet tank, faded to obscurity with little information on it past its development period. It was the heaviest of the Soviet heavy tanks that were slated for a production. The IS-4's design was further developed on in the IS tank family with the ''Object 703'', with the design using an electrical transmission instead of a mechanical one. This vehicle, redesignated the ''[[IS-6]]'', also proved to be problematic and was shelved.<ref name="ZalogaIS"/> | + | The IS-4, as a relatively unsuccessful Soviet tank, faded to obscurity with little information on it past its development period. It was the heaviest of the Soviet heavy tanks that were slated for a production. The IS-4's design was further developed on in the IS tank family with the ''Object 703'', with the design using an electrical transmission instead of a mechanical one. This vehicle, redesignated the ''[[IS-6]]'', also proved to be problematic and was shelved.<ref name="ZalogaIS" /> |
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| Line 246: | Line 252: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''reference to the series of the vehicles;'' | * ''reference to the series of the vehicles;'' | ||
* ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' | * ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' | ||
| Line 251: | Line 258: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
* ''encyclopedia page on tank;'' | * ''encyclopedia page on tank;'' | ||
Revision as of 12:37, 12 March 2019
Contents
Description
The IS-4M is a Rank Soviet heavy tank
with a battle rating of (AB), (RB), and (SB). It was introduced during the closed beta testing for Ground Forces before Update 1.41.
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour (Hull, Turret roof, Hatch roof)
- Cast homogeneous armour (Turret)
| Armour | Front | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 140 mm (62°) Front glacis 160 mm (40°) Lower glacis 160 mm (34-77°) Driver's port 40 mm (44-87°) Top of Driver's port |
160 mm (30-53°) Top 160 mm Middle 30 mm (61°) Bottom |
100 mm (37°) Top 30 mm (80°) Middle 100 mm (31-39°) Bottom |
30 mm |
| Turret | 200-250 mm (2-89°) Turret front 200 mm (0-65°) , 170 + 250 mm (2-61°) Gun mantlet |
200 mm (3-40°) | 150 (62-72°) Top 170 mm (21-49°) Bottom |
30 mm Front, Hatch roof, Ventilators 50 mm Front sides 170 mm Center |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels are 20 mm thick, torsion bars are 10 mm thick, and tracks are 30 mm thick.
Mobility
| Mobility characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Weight (tons) | Add-on Armour weight (tons) |
Max speed (km/h) |
| 60.0 | N/A | 45 (AB) |
| 43 (RB/SB) | ||
| Engine power (horsepower) | ||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded |
| Arcade | 968 | ___ |
| Realistic/Simulator | 663 | 750 |
| Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | ||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded |
| Arcade | 16.13 | __.__ |
| Realistic/Simulator | 11.05 | 12.50 |
Armaments
Main armament
| 122 mm D-25T | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance |
Stabilizer | ||
| 30 | -3°/+19° | ±180° | N/A | ||
| Turret rotation speed (°/s) | |||||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. |
| Arcade | 8.1 | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ |
| Realistic | 5.9 | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ |
| Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||
| Stock | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. | ||
| 27.1 | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ | ||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration in mm @ 90° | |||||
| 10m | 100m | 500m | 1000m | 1500m | 2000m | ||
| BR-471 | APHE | 204 | 200 | 182 | 162 | 144 | 128 |
| BR-471B | APHEBC | 205 | 202 | 191 | 178 | 165 | 154 |
| BR-471D | APCBC | 229 | 227 | 214 | 199 | 186 | 173 |
| OF-471 | HE | 45 | 45 | 44 | 43 | 42 | 42 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity in m/s |
Projectile Mass in kg |
Fuse delay
in m: |
Fuse sensitivity
in mm: |
Explosive Mass in g (TNT equivalent): |
Normalization At 30° from horizontal: |
Ricochet: | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||
| BR-471 | APHE | 795 | 25 | 1.2 | 15 | 272 | -1° | 47° | 60° | 65° |
| BR-471B | APHEBC | 795 | 25 | 1.2 | 15 | 272 | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| BR-471D | APCBC | 800 | 25 | 1.2 | 15 | 212.5 | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| OF-471 | HE | 800 | 25 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 3,600 | +0° | 79° | 80° | 81° |
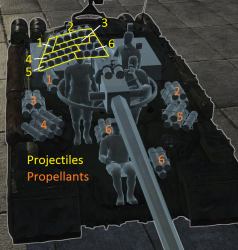
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
Ammo Part |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
6th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | Projectiles Propellants |
29 (+1) 29 (+1) |
24 (+6) 24 (+6) |
19 (+11) 19 (+11) |
14 (+16) 14 (+16) |
9 (+21) 9 (+21) |
1 (+29) 1 (+29) |
no |
Machine guns
| 12.7 mm DShK | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pintle mount | ||||||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) |
Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance | |||
| 250 (50) | 600 | -10°/+60° | ±180° | |||
| Coaxial mount | ||||||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) |
Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance | |||
| 1,000 (50) | 600 | N/A | N/A | |||
Usage in battles
Describe the tactics of playing in the vehicle, the features of using vehicles in the team and advice on tactics. Refrain from creating a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view but give the reader food for thought. Describe the most dangerous enemies and give recommendations on fighting them. If necessary, note the specifics of the game in different modes (AB, RB, SB).
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Very good frontal armour; can even bounce 128 mm shells from the Maus.
- Retains the powerful D-25T 122mm gun as on the previous IS-2 and IS-3
- The mere presence of an IS-4 can make enemies panic or run and hide.
- Slightly wider choices of ammo compared to the IS-2 and IS-3.
Cons:
- Can - and will - be a priority target for the enemy team due to its fearsome reputation
- Long reload of 20 seconds
- Ammo rack in back of the turret; if a shell penetrates, the ammo could detonate.
History
Development
During the development of the IS-3 in 1944 under General Nikolai Dukhov, a separate project was underway by a design team led by L.S. Troyanov to improve the IS-2 design. This separate project commenced under the designation Object 701. The project produced three proposed design. The Object 701-2 with a S-34 100 mm gun, 701-5 with a different armour configuration, and the 701-6 with the 122 mm D-25 gun. The 701-6 was accepted for further development, to which was modified with thicker armour, longer hull, and a more powerful engine. There was some implementation of German designs into the prototype; the engine has a cooling system that uses a pair of circular fans on the engine deck, a feature also seen on the Panther tank.[1]
Usage
Object 701 was eventually approved for production in 1947 as the IS-4. The production turned out 200 tanks (some sources say 250) before the production was halted. The reason being that the IS-4 was criticized for being inadequate in mobility despite its new engine.[1] While production ended, the remaining IS-4 still saw service in the Soviet Union. When the Korean War broke out in 1950 and the United States and its allies got involved, the IS-4s were all shipped to the Far East of the Soviet Union in anticipation of Soviet intervention in the Korean War. They were not committed despite pressure by the Chinese from fear of inciting another world war. Even so, the IS-4 stayed in the region ready for action. In the late 1950s, the IS-4 underwent a modernization program along the lines of the IS-3 with increased ammo stowage, new machine gun armaments, new gun optics, better engine, and better filtration system and this modernized variant was named the IS-4M.[1] The IS-4 stayed in service in the Soviet Union until the 1960s.
Legacy
The IS-4, as a relatively unsuccessful Soviet tank, faded to obscurity with little information on it past its development period. It was the heaviest of the Soviet heavy tanks that were slated for a production. The IS-4's design was further developed on in the IS tank family with the Object 703, with the design using an electrical transmission instead of a mechanical one. This vehicle, redesignated the IS-6, also proved to be problematic and was shelved.[1]
Media
Camouflages and skins for the IS-4 from live.warthunder.com
References
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:
- topic on the official game forum;
- encyclopedia page on tank;
- other literature.
| USSR heavy tanks | |
|---|---|
| KV-1 | KV-1 (L-11) · KV-1 (ZiS-5) · KV-1E · KV-1S |
| KV-2 | KV-2 (1939) · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) |
| Other KVs | KV-85 · KV-122 · KV-220 |
| IS-1/2 | IS-1 · IS-2 · IS-2 (1944) · IS-2 No.321 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 |
| Other IS tanks | IS-3 · IS-4M · IS-6 · IS-7 |
| T-10 | T-10A · T-10M |
| Multi-turreted | T-35 · SMK |
| Other | Object 279 |
| Lend-Lease | ▂MK-II "Matilda" |