Difference between revisions of "T-72B"
(→Main armament) (Tag: Visual edit) |
m (→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{About | {{About | ||
| about = Soviet medium tank '''{{PAGENAME}}''' | | about = Soviet medium tank '''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| − | | usage = | + | | usage = other versions |
| − | | link = T- | + | | link = T-72 (Family) |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Specs-Card | ||
| + | |code=ussr_t_72b | ||
| + | |images={{Specs-Card-Image|GarageImage_{{PAGENAME}}.jpg}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
<!-- ''In the description, the first part should be about the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle, as well as its key features. In the second part, tell the reader about the ground vehicle in the game. Insert a screenshot of the vehicle, so that if the novice player does not remember the vehicle by name, he will immediately understand what kind of vehicle the article is talking about.'' --> | <!-- ''In the description, the first part should be about the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle, as well as its key features. In the second part, tell the reader about the ground vehicle in the game. Insert a screenshot of the vehicle, so that if the novice player does not remember the vehicle by name, he will immediately understand what kind of vehicle the article is talking about.'' --> | ||
| − | + | The '''T-72B''' is the third variant of the [[T-72 (Family)|T-72 main battle tank family]]. This features many improvements compared to its predecessors. A cutting-edge 125 mm 2A46M tank gun with a newly developed two-plane fully automatic stabilization system known as 2E42-2 has been installed. A significantly improved 1A40-1 fire control system, as well as the 1K13-49 gunner's sight for firing the 9M119 Svir anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) through the gun barrel, have also been added. To increase protection, 20 mm of appliqué armour was mounted on the front of the hull. The mobility upgrade package included a new V-84-1 engine with 840 horsepower. The smoke dischargers, which were previously mounted on the turret front as on the T-72A variant, were later grouped on the turret's left side to make room for the installation of explosive reactive armour (ERA). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | The ''' | + | Introduced in [[Update 1.97 "Viking Fury"]], the T-72B tank is powerful and competitive. The turret and hull provide excellent protection. However, it continues to lag behind its Western counterparts in mobility and lacks thermal imaging equipment for quick target acquisition. One of the most significant disadvantages is the slow reverse speed, which makes close-range engagements risky. Overall, this tank is effective in support, flanking, and sniping roles. It is critical to keep some distance from the main contested zones to fully utilize its strong frontal armour. |
== General info == | == General info == | ||
=== Survivability and armour === | === Survivability and armour === | ||
| + | {{Specs-Tank-Armour}} | ||
<!-- ''Describe armour protection. Note the most well protected and key weak areas. Appreciate the layout of modules as well as the number and location of crew members. Is the level of armour protection sufficient, is the placement of modules helpful for survival in combat? If necessary use a visual template to indicate the most secure and weak zones of the armour.'' --> | <!-- ''Describe armour protection. Note the most well protected and key weak areas. Appreciate the layout of modules as well as the number and location of crew members. Is the level of armour protection sufficient, is the placement of modules helpful for survival in combat? If necessary use a visual template to indicate the most secure and weak zones of the armour.'' --> | ||
| − | The T-72B is an up-armoured and up-gunned version of the T-72A | + | The T-72B is an up-armoured and up-gunned version of the T-72A, although this still does not protect the "weak spots" that most Soviet tanks have (weak lower front plate, driver optics etc.). The T-72B has more armour on the upper plate of the hull, that provides around 500 mm to 900 mm of effective armour protection. |
| + | |||
| + | '''Armour type:''' <!-- The types of armour present on the vehicle and their general locations --> | ||
| + | <!-- Example: * Rolled homogeneous armour (Front, Side, Rear, Hull roof) | ||
| + | * Cast homogeneous armour (Turret, Transmission area) --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Armour !! Front (Slope angle) !! Sides !! Rear !! Roof | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Hull || 60 mm (60°) || 80 mm ''Top'' <br> 20 mm ''Bottom'' || 40 mm || 20 - 30 mm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Turret || Variable thickness armour ''Turret front'' <br> 220-600 mm ''Gun mantlet'' || 240 - 118 mm || 60 - 115 mm || 45 mm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Cupola || 100 mm (variable angles) || 100 mm || 100 mm || 40 mm | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Notes:''' <!-- Any additional notes which the user needs to be aware of --> | ||
| + | <!-- Example: * Suspension wheels are 20 mm thick, tracks are 30 mm thick, and torsion bars are 60 mm thick. --> | ||
=== Mobility === | === Mobility === | ||
| + | {{Specs-Tank-Mobility}} | ||
<!-- ''Write about the mobility of the ground vehicle. Estimate the specific power and manoeuvrability, as well as the maximum speed forwards and backwards.'' --> | <!-- ''Write about the mobility of the ground vehicle. Estimate the specific power and manoeuvrability, as well as the maximum speed forwards and backwards.'' --> | ||
{{tankMobility|abMinHp=1,302|rbMinHp=743}} | {{tankMobility|abMinHp=1,302|rbMinHp=743}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The T-72B is a slow and sluggish tank which has poor acceleration and handling. It has really poor reverse speed as well as hull traverse. However, it has a powerful engine which makes it capable of pulling and pushing enemy tanks as well as moving through rough terrain with ease. It does not have enough horsepower to climb over steep elevations. Speed-wise, it has a decent top speed (~60-70 km/h) which it can reach under specific situations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Modifications and economy === | ||
| + | {{Specs-Economy}} | ||
== Armaments == | == Armaments == | ||
| + | {{Specs-Tank-Armaments}} | ||
=== Main armament === | === Main armament === | ||
| + | {{Specs-Tank-Weapon|1}} | ||
<!-- ''Give the reader information about the characteristics of the main gun. Assess its effectiveness in a battle based on the reloading speed, ballistics and the power of shells. Do not forget about the flexibility of the fire, that is how quickly the cannon can be aimed at the target, open fire on it and aim at another enemy. Add a link to the main article on the gun: <code><nowiki>{{main|Name of the weapon}}</nowiki></code>. Describe in general terms the ammunition available for the main gun. Give advice on how to use them and how to fill the ammunition storage.'' --> | <!-- ''Give the reader information about the characteristics of the main gun. Assess its effectiveness in a battle based on the reloading speed, ballistics and the power of shells. Do not forget about the flexibility of the fire, that is how quickly the cannon can be aimed at the target, open fire on it and aim at another enemy. Add a link to the main article on the gun: <code><nowiki>{{main|Name of the weapon}}</nowiki></code>. Describe in general terms the ammunition available for the main gun. Give advice on how to use them and how to fill the ammunition storage.'' --> | ||
| − | {{main|2A46M | + | {{main|2A46M (125 mm)}} |
The T-72B is armed with the same 125 mm cannon found in the [[T-80B]], with its 3BM42 "Mango" round proving competitive against other Rank VII offerings. As with previous Russian MBTs, the main gun is auto-loaded, so the loss of a crew member does not affect the loading times and the 7.1-second loading speed is competitive when compared to the 120 mm guns on the Leopard 2A5 and M1A2 Abrams. One notable perk of the auto-loader mechanism is that the gun will be reloaded even if the gunner is knocked out, if you're fighting a fire, or repairing. It does however also come with the drawbacks of a reload time that cannot be improved, the large ammo carousel concentric with the turret, and the chance of a single penetrating shot detonating the ammo racks. Another thing to note, since update 1.97 if the tank's battery runs out of power, the auto loader will not function and the cannon will need to be manually loaded, which is a much slower process. | The T-72B is armed with the same 125 mm cannon found in the [[T-80B]], with its 3BM42 "Mango" round proving competitive against other Rank VII offerings. As with previous Russian MBTs, the main gun is auto-loaded, so the loss of a crew member does not affect the loading times and the 7.1-second loading speed is competitive when compared to the 120 mm guns on the Leopard 2A5 and M1A2 Abrams. One notable perk of the auto-loader mechanism is that the gun will be reloaded even if the gunner is knocked out, if you're fighting a fire, or repairing. It does however also come with the drawbacks of a reload time that cannot be improved, the large ammo carousel concentric with the turret, and the chance of a single penetrating shot detonating the ammo racks. Another thing to note, since update 1.97 if the tank's battery runs out of power, the auto loader will not function and the cannon will need to be manually loaded, which is a much slower process. | ||
| − | As with the T-80B and T-64B, the T-72B can launch missiles out of its gun. Unlike the previous two vehicles though, it gets the upgraded 9M119 which has 700 mm of penetration compared to the previous ATGM's 650 mm penetration. These | + | As with the T-80B and T-64B, the T-72B can launch missiles out of its gun. Unlike the previous two vehicles though, it gets the upgraded 9M119 which has 700 mm of penetration compared to the previous ATGM's 650 mm penetration. These ATGMs can prove useful for shooting over hills to hit a hiding enemy or to engage helicopters or low-flying aircraft. |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="100%" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="100%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! colspan="5" | [[2A46M | + | ! colspan="5" | [[2A46M (125 mm)|125 mm 2A46M]] || colspan="5" | Turret rotation speed (°/s) || Reloading rate (seconds) |
|- | |- | ||
! Mode !! Capacity !! Vertical !! Horizontal !! Stabilizer | ! Mode !! Capacity !! Vertical !! Horizontal !! Stabilizer | ||
! Stock !! Upgraded !! Full !! Expert !! Aced | ! Stock !! Upgraded !! Full !! Expert !! Aced | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Autoloader |
|- | |- | ||
! ''Arcade'' | ! ''Arcade'' | ||
| − | | rowspan="2" | 45 || rowspan="2" | - | + | | rowspan="2" | 45 || rowspan="2" | -5°/+13° || rowspan="2" | ±180° || rowspan="2" | Two-plane || 22.8 || 31.6 || 38.4 || 42.5 || 45.2 || rowspan="2" | 7.10 |
|- | |- | ||
! ''Realistic'' | ! ''Realistic'' | ||
| − | | 14.3 || 16.8 ||20.4||22.6||24.0 | + | | 14.3 || 16.8 || 20.4 || 22.6 || 24.0 |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==== Ammunition ==== | ==== Ammunition ==== | ||
| − | { | + | {{:2A46M (125 mm)/Ammunition|3BK18M, 3OF26, 3BM22, 9M119, 3BM42}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | { | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | 3BK18M | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== [[Ammo racks]] ==== | ==== [[Ammo racks]] ==== | ||
| − | + | [[File:Ammoracks_{{PAGENAME}}.png|right|thumb|x250px|[[Ammo racks]] of the {{PAGENAME}}]] | |
| + | <!-- '''Last updated:''' --> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 104: | Line 91: | ||
! 3rd<br>rack empty | ! 3rd<br>rack empty | ||
! 4th<br>rack empty | ! 4th<br>rack empty | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
! Visual<br>discrepancy | ! Visual<br>discrepancy | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | '''45''' || | + | | '''45''' || 41 ''(+4)'' || 34 ''(+11)'' || 22 ''(+23)'' || 0 ''(+45)'' || No |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Machine guns === | === Machine guns === | ||
| + | {{Specs-Tank-Weapon|2}} | ||
| + | {{Specs-Tank-Weapon|3}} | ||
<!-- ''Offensive and anti-aircraft machine guns not only allow you to fight some aircraft but also are effective against lightly armoured vehicles. Evaluate machine guns and give recommendations on its use.'' --> | <!-- ''Offensive and anti-aircraft machine guns not only allow you to fight some aircraft but also are effective against lightly armoured vehicles. Evaluate machine guns and give recommendations on its use.'' --> | ||
{{main|NSVT (12.7 mm)|PKT (7.62 mm)}} | {{main|NSVT (12.7 mm)|PKT (7.62 mm)}} | ||
| − | The T-72B has access to a coaxial PKT 7. | + | The T-72B has access to a coaxial PKT 7.62 mm machine gun and a 12.7 mm NSVT anti-aircraft machine gun, which is mounted above the commander's hatch. The PKT is rarely useful in top tier matches, but the NSVT can be quite useful. The NSVT has 29 mm of penetration, allowing it to damage some light vehicles like IFVs and enemy SPAA. Additionally it is useful to engage enemy helicopters when they come close. Machine guns can also be used to try and shoot down enemy ATGMs, but this is unreliable. They can also be used to shoot the ground in front of the tank for a quick smoke screen of sorts, confusing the enemy and blocking their view for a clean shot. |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="50%" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="50%" | ||
| Line 124: | Line 111: | ||
! Mount !! Capacity (Belt) !! Fire rate !! Vertical !! Horizontal | ! Mount !! Capacity (Belt) !! Fire rate !! Vertical !! Horizontal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Pintle || 300 ( | + | | Pintle || 300 (60) || 700 || -4°/+75° || ±180° |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 133: | Line 120: | ||
! Mount !! Capacity (Belt) !! Fire rate !! Vertical !! Horizontal | ! Mount !! Capacity (Belt) !! Fire rate !! Vertical !! Horizontal | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Coaxial || 2,000 (250) || 700 || | + | | Coaxial || 2,000 (250) || 700 || - || - |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Usage in battles == | == Usage in battles == | ||
| − | ''Describe the tactics of playing in the vehicle, the features of using vehicles in the team and advice on tactics. Refrain from creating a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view but instead give the reader food for thought. Describe the most dangerous enemies and give recommendations on fighting them. If necessary, note the specifics of the game in different modes (AB, RB, SB).'' | + | <!-- ''Describe the tactics of playing in the vehicle, the features of using vehicles in the team and advice on tactics. Refrain from creating a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view but instead give the reader food for thought. Describe the most dangerous enemies and give recommendations on fighting them. If necessary, note the specifics of the game in different modes (AB, RB, SB).'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | There are three main ways to use the T-72B: as a flanker, as a sniper, or as a frontline support tank. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Flanking === | ||
| + | The T-72B performs awesomely as a flanker, especially with the new engine. In many maps, such as Berlin, Maginot Line or Mozdok, it will be one of the best playstyles. If APFSDS hasn't been researched yet, try to know the locations of your most common opponents' ammo racks (i.e. [[XM-1 (Chrysler)]]/[[XM-1 (GM)|(GM)]], [[T-72AV (TURMS-T)|T-72 TURMS]] and [[Leopard 1 (Family)|Leopards 1]]/[[Leopard 2 (Family)|2]]), and aim at them, since HEAT-FS doesn't feature great damage against composite armours. When facing multiple enemies, prioritise disabling them (destroying gun breech/barrel, knocking out gunner, etc.) so that they don't pose an immediate threat and you can destroy them later. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Sniping === | ||
| + | This is another great performance of the T-72, as it has adequate shell velocity and penetration. HEAT-FS penetrates 550 mm of armour at any distance, and its muzzle speed is faster than most of other HEAT-FS shell you will meet. Also, the APFSDS performs excellently because of its extreme velocity (~1,760 m/s) and high penetration (425 mm). Try to keep a distance of at least 1 km and no more than 1.5 km when using HEAT, but the unlocking of sabot shells will increase your range almost indefinitely. Try to cover your lower glacis, as it is your only weakspot at range. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Frontline support === | ||
| + | This playstyle is very risky, as your slow reverse speed will turn your tank into a coffin, but with access to the 3BM42 shot, it will become more viable. Do not, ever, do this alone. Always try to have at least two reliable teammates covering you. Your main goal in this playstyle is to cover offensives, and defend and attack bases. Cover weaker tanks by attracting fire and secure base capturers. In this mode, you should not focus on making experience for your own, like capturing bases, but to ensure the achievement of victory. This style will mostly take your tank as sacrifice, unless played very carefully and prudently, but victory multipliers will overcome your losses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Enemies worth noting:''' | ||
| − | + | * [[XM-1 (Chrysler)]]/[[XM-1 (GM)|(GM)]]: Avoid attempting combat with the 3BK18M HEATFS shells, despite their having thin composite armour | |
| − | + | * [[AMX-30B2]]/[[AMX-30B2 BRENUS]]: DM23/33 have enough armour penetration to penetrate T-72 driver frontal plates, though all shells are effective against them in return. | |
| − | + | * [[Leopard 2K]]: Turret mantlet is resistant to 3BK18M. | |
| − | + | * [[AMX-40]]: Turret mantlet and lower frontal plate are highly resistant to 3BK18M. | |
| − | + | * [[Strv 103 (Family)|Strv 103]]: Depending on the hull angling, HEAT-FS rounds such as the 3BK18M might ricochet. APFSDS is recommended to be used when facing it frontally. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | 3BK18M | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Pros and cons === | === Pros and cons === | ||
| Line 186: | Line 151: | ||
'''Pros:''' | '''Pros:''' | ||
| − | * Excellent armour protection | + | * Excellent composite armour protection |
| − | * CONTACT-1 ERA coverage to front and sides | + | * Turret cheeks will chew up modern-day tank shells, invulnerable even to the mighty DM53 |
| + | * CONTACT-1 ERA coverage to front and sides, provides great protection against chemical shells (~400 mm) | ||
* Powerful main armament with autoloader, 3BM42 round, and laser rangefinder | * Powerful main armament with autoloader, 3BM42 round, and laser rangefinder | ||
| − | + | * Barrel launched ATGMs, without extra reload time | |
| − | * Barrel launched ATGMs | ||
* ESS and smoke grenades | * ESS and smoke grenades | ||
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| − | * | + | * Extremely prone to gun breech disabling, as in all post-war T-series |
| − | * Lack of thermals at rank | + | * Very bad reverse speed (-4 km/h) |
| − | * | + | * Lack of thermals at rank VII |
| − | * | + | * ERA provides insignificant protection against kinetic shells (~5 mm) |
| + | * Side armour is so thin that can be penetrated basically at any angle, which will inevitably ammo-rack you | ||
| + | * Small crew count, cramped interior and large ammo rack mean low survivability | ||
| + | * Poor gun depression | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | ''Describe the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the vehicle and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Vehicle-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>. This section may also include the vehicle's dev blog entry (if applicable) and the in-game encyclopedia description (under <code><nowiki>=== In-game description ===</nowiki></code>, also if applicable).'' | + | <!-- ''Describe the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the vehicle and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Vehicle-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>. This section may also include the vehicle's dev blog entry (if applicable) and the in-game encyclopedia description (under <code><nowiki>=== In-game description ===</nowiki></code>, also if applicable).'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | The T-72 was one of the most famous and widely produced Soviet main battle tanks of the Cold War era. Originating as a modification of the [[T-64A (1971)|T-64]], the T-72 retained its predecessor's composite armour, 125 mm smoothbore cannon, and compact dimensions, all modern features for the time. But it was intended to be easier to produce and maintain than the complex and unreliable T-64. Instead of the T-64's opposed piston engine, which promised high power in a compact package but turned out to be a mechanical nightmare, the T-72 used a more traditional V-46 engine with larger dimensions. The engine compartment and suspension were redesigned to suit the new engine. The original T-64 "MZ" autoloader was replaced with the "AZ" autoloader, which stored ammunition in two horizontal trays. The T-72 began to equip standard tank divisions and motorized units while elite units retained the T-64. The combat capabilities of the initial T-72 were very close despite its origin as a somewhat simplified T-64, as the heavier weight was compensated for by the greater engine power. The T-64 tended to have more advanced optics and fire control systems over its service life, and the later T-80 had much superior mobility, but the simple cost effectiveness and reliability of the T-72 made it an excellent tank for widespread deployment and export. It remains in service worldwide in many different variants and has arguably been a more successful design than its ostensibly higher-tech relatives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''T-72B''' variant first appeared in 1985. At this time, the preceding [[T-72A]] had shown its age. The newest NATO tanks had guns and ammunition capable of penetrating early Soviet composite armour and the T-72A's fire control system was lacking. The [[T-64B]], introduced several years earlier, had improved armour and a new fire control system capable of supporting gun-launched ATGMs like the 9M112 "Kobra". The T-72B set out to meet these standards. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As part of the improvements, the protection was improved dramatically. The turret was constructed with high hardness steel and improved "Super Dolly Parton" composite armour that bulged the turret cheeks even further. The increased volume necessitated cuts underneath the turret cheeks/sides to allow the driver to open his hatch if the turret was rotated. The composite armour used polymer and steel NERA layers much like the [[Leopard 2A4|Leopard 2]] and [[M1 Abrams]] instead of the "Kvartz" ceramic filler used on earlier T-72As. This provided improved chemical protection on par with these two NATO MBTs and also easier serviceability: the NERA plates could be accessed and replaced in the field if damaged, whereas the sintered quartz blocks were cast with the turret in the factory and could not be repaired. Kinetic protection was increased to a reported figure of 550 mm RHA equivalent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The hull composite armour was switched to a new 60-10-10-20-20-50 configuration: a 60 mm front plate, four high hardness plates of 10 mm and 20 mm thickness, and a 50 mm back plate. While this is technically spaced armour instead of composite armour, it offered significant improvements in kinetic protection over the older textolite composition. In fact, comparative testing of the T-72B's glacis armour and the [[T-80B|T-80BV]]'s configuration showed that it was immune to even overpressure shots using 3BM32 "Vant" depleted uranium APFSDS, which penetrated the T-80BV using standard charges. Chemical protection was also improved and the T-72B's upper glacis was capable of resisting HEAT-FS rounds, man-portable ATGMs, and older full-size ATGMs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The armour upgrades played a large role in increasing the T-72B's weight to about 43 tons at combat weight compared to the T-72A's 41 tons. To cope with this, a V-84 engine producing 840 horsepower was installed. It was a close derivative of the V-46 and in theory should have been very easy to retrofit to existing T-72s. However, its increased power and heat generation required modifications to the T-72B design. An engineer recalled that the V-84 somehow developed less power than the V-46 when installed in the T-72A. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The T-72B received a new 1A40-1 sighting complex with a lead calculator, improved laser rangefinder, and support for 9M119 "Svir" gun-launched ATGMs through an improved night sight. The gunner could lase a moving target while looking down the sight and the system would calculate and display how many mils to lead by in a secondary eyepiece. From the gunner's view, the calculation result would be superimposed on the sight view. This made it easier for the tank to engage moving targets, which previously was unassisted on early T-72A models, but the system was not precise enough for reliable long distance shooting and lagged behind the [[M60A3 TTS|M60A3]]'s fire control system in ease of use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other minor changes included modifications to the autoloader to accommodate the Svir ATGMs and an improved 2E42-2 "Zhasmin" stabilizer system with an electric drive instead of hydraulics. The vehicle represented in War Thunder is equipped with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour, which became standard for T-72Bs out of the factory. The turret ERA was no longer mounted on brackets as on the [[T-64B]] or T-72AV, instead being placed directly on the turret surface. This more haphazard arrangement increased the coverage of the ERA but slightly decreased effectiveness due to suboptimal sloping towards incoming fire. Still, a T-72B with Kontakt-1 was virtually immune to single-charge chemical munitions. [[T-72B (1989)|Later production variants]] were capable of equipping improved Kontakt-5 ERA, which in turn made them resistant to even the best NATO APFSDS rounds at the time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The T-72B successfully addressed the immediate problems facing the T-72A. The protection now matched or exceeded the new NATO MBTs that were capable of dispatching the previous model and the fire control upgrades provided a welcome increase in offensive capabilities. This was achieved without sacrificing ease of production and the T-72B was widely produced and exported like prior models. No improvements were made to its mobility, which was now exceeded by the Abrams and Leopard 2, and the fire control system was still inferior to Western tanks. Still, it provided a solid foundation for modernizations like the [[T-72B3]] and will likely stay in service for the next few decades. The famous T-90 had its beginnings as an upgraded "T-72BU" as well. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The T-72B did not see any combat with the Soviet Union. The succeeding Russian Federation has used the T-72B in Chechenya, Georgia, and elsewhere. Other customers and current users of the T-72B include Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Laos, Morocco, and Syria. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[wt:en/news/6614-development-t-72b-necessary-improvements-en|Devblog]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | By the middle of the 1980s, there was an objective need to upgrade the main battle tank of the Soviet Union - T-72 to modern battle performance values. The fact is that the vehicle seriously lacked firepower and modern fire control systems and its protection which wasn't bad at the time of conception, became obsolete due to the emergence of new powerful weapons. The big tank modernization program implied a comprehensive improvement of the T-72 in all its key characteristics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the early 80s, the guided weapon system under the name "Svir" was developed for the Soviet tanks with the ability to guide the missile via beam and launching it through the gun barrel. At the same time there was also work on development of the first generation of the "Contact-1" explosive reactive armour. Both of these novelties were in demand for the modernization of the T-72. The vehicle received a new combined hull armour pack for the upper frontal part which increases in size and its composition has been redistributed toward more steel. Also a new custom turret with larger dimensions has been installed, featuring new armour filler packs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Due to an increased weight, the tank required a new engine which allowed it to maintain the good running characteristics of the base model. The upgraded version received the designation T-72B and was adopted in December 1984. This modification became the basis for a large number of versions and upgrades which made the T-72 the most mass produced 2nd generation MBT in the world. As an upgraded version this tank continues to serve in the Russian army and many other countries. | ||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
<!-- ''Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.'' --> | <!-- ''Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.'' --> | ||
| − | {{Youtube-gallery|V3Gfl_N4JV8|'''The Shooting Range #192''' - ''Metal Beasts'' section at 00:32 discusses the T-72B.}} | + | |
| + | ;Skins | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://live.warthunder.com/feed/camouflages/?vehicle=ussr_t_72b Skins and camouflages for the {{PAGENAME}} from live.warthunder.com.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Images | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed" heights="150"> | ||
| + | File:T-72B WTWallpaper 01.jpg| | ||
| + | File:T-72B WTWallpaper 02.jpg| | ||
| + | File:T-72B WTWallpaper 03.jpg| | ||
| + | File:T-72B WTWallpaper 04.jpg| | ||
| + | File:T-72B WTWallpaper 05.jpg| | ||
| + | File:T-72B WTWallpaper 06.jpg| | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Videos | ||
| + | {{Youtube-gallery|LufGqZTfvoI|'''MBTs with Best Armor''' discusses the {{PAGENAME}} at 04:42 - ''War Thunder Official Channel''|V3Gfl_N4JV8|'''The Shooting Range #192''' - ''Metal Beasts'' section at 00:32 discusses the T-72B.}} | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| Line 216: | Line 226: | ||
<!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | <!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | ||
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
| − | |||
* ''other literature.'' --> | * ''other literature.'' --> | ||
* [[wt:en/news/6614-development-t-72b-necessary-improvements-en|[Devblog] T-72B: Necessary Improvements]] | * [[wt:en/news/6614-development-t-72b-necessary-improvements-en|[Devblog] T-72B: Necessary Improvements]] | ||
| + | {{TankManufacturer Uralvagonzavod}} | ||
{{USSR medium tanks}} | {{USSR medium tanks}} | ||
| + | [[Category:ATGM vehicles]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:04, 6 January 2024
| This page is about the Soviet medium tank T-72B. For other versions, see T-72 (Family). |
Contents
Description
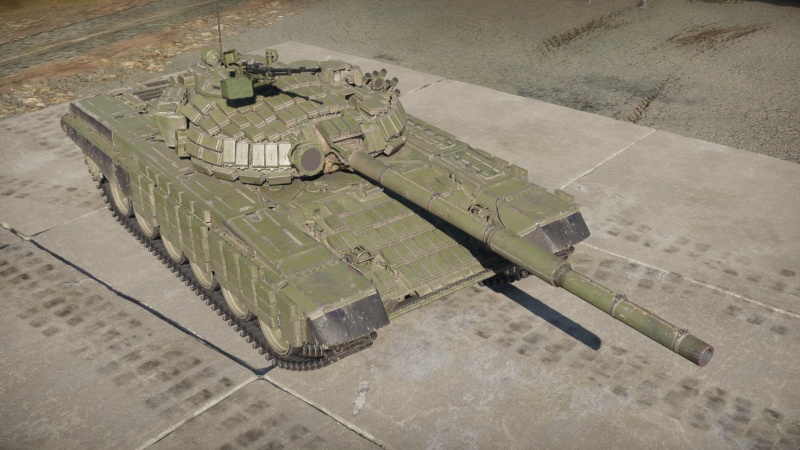
The T-72B is the third variant of the T-72 main battle tank family. This features many improvements compared to its predecessors. A cutting-edge 125 mm 2A46M tank gun with a newly developed two-plane fully automatic stabilization system known as 2E42-2 has been installed. A significantly improved 1A40-1 fire control system, as well as the 1K13-49 gunner's sight for firing the 9M119 Svir anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) through the gun barrel, have also been added. To increase protection, 20 mm of appliqué armour was mounted on the front of the hull. The mobility upgrade package included a new V-84-1 engine with 840 horsepower. The smoke dischargers, which were previously mounted on the turret front as on the T-72A variant, were later grouped on the turret's left side to make room for the installation of explosive reactive armour (ERA).
Introduced in Update 1.97 "Viking Fury", the T-72B tank is powerful and competitive. The turret and hull provide excellent protection. However, it continues to lag behind its Western counterparts in mobility and lacks thermal imaging equipment for quick target acquisition. One of the most significant disadvantages is the slow reverse speed, which makes close-range engagements risky. Overall, this tank is effective in support, flanking, and sniping roles. It is critical to keep some distance from the main contested zones to fully utilize its strong frontal armour.
General info
Survivability and armour
The T-72B is an up-armoured and up-gunned version of the T-72A, although this still does not protect the "weak spots" that most Soviet tanks have (weak lower front plate, driver optics etc.). The T-72B has more armour on the upper plate of the hull, that provides around 500 mm to 900 mm of effective armour protection.
Armour type:
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 60 mm (60°) | 80 mm Top 20 mm Bottom |
40 mm | 20 - 30 mm |
| Turret | Variable thickness armour Turret front 220-600 mm Gun mantlet |
240 - 118 mm | 60 - 115 mm | 45 mm |
| Cupola | 100 mm (variable angles) | 100 mm | 100 mm | 40 mm |
Notes:
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | Expression error: Unexpected * operator. | 1,302 | Expression error: Unexpected round operator. | __.__ | |||
| Realistic | 743 | Expression error: Unexpected round operator. | __.__ | ||||
The T-72B is a slow and sluggish tank which has poor acceleration and handling. It has really poor reverse speed as well as hull traverse. However, it has a powerful engine which makes it capable of pulling and pushing enemy tanks as well as moving through rough terrain with ease. It does not have enough horsepower to climb over steep elevations. Speed-wise, it has a decent top speed (~60-70 km/h) which it can reach under specific situations.
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
The T-72B is armed with the same 125 mm cannon found in the T-80B, with its 3BM42 "Mango" round proving competitive against other Rank VII offerings. As with previous Russian MBTs, the main gun is auto-loaded, so the loss of a crew member does not affect the loading times and the 7.1-second loading speed is competitive when compared to the 120 mm guns on the Leopard 2A5 and M1A2 Abrams. One notable perk of the auto-loader mechanism is that the gun will be reloaded even if the gunner is knocked out, if you're fighting a fire, or repairing. It does however also come with the drawbacks of a reload time that cannot be improved, the large ammo carousel concentric with the turret, and the chance of a single penetrating shot detonating the ammo racks. Another thing to note, since update 1.97 if the tank's battery runs out of power, the auto loader will not function and the cannon will need to be manually loaded, which is a much slower process.
As with the T-80B and T-64B, the T-72B can launch missiles out of its gun. Unlike the previous two vehicles though, it gets the upgraded 9M119 which has 700 mm of penetration compared to the previous ATGM's 650 mm penetration. These ATGMs can prove useful for shooting over hills to hit a hiding enemy or to engage helicopters or low-flying aircraft.
| 125 mm 2A46M | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Autoloader |
| Arcade | 45 | -5°/+13° | ±180° | Two-plane | 22.8 | 31.6 | 38.4 | 42.5 | 45.2 | 7.10 |
| Realistic | 14.3 | 16.8 | 20.4 | 22.6 | 24.0 | |||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| 3BK18M | HEATFS | 550 | 550 | 550 | 550 | 550 | 550 |
| 3OF26 | HE | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 |
| 3BM22 | APFSDS | 425 | 420 | 415 | 405 | 393 | 380 |
| 9M119 | ATGM | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 |
| 3BM42 | APFSDS | 457 | 454 | 445 | 431 | 419 | 406 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (kg) |
Ricochet | |||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| 3BK18M | HEATFS | 905 | 19 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 2.79 | 65° | 72° | 77° | |||
| 3OF26 | HE | 850 | 23 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 5.24 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |||
| 3BM22 | APFSDS | 1,760 | 4.83 | - | - | - | 76° | 77° | 80° | |||
| 3BM42 | APFSDS | 1,700 | 4.85 | - | - | - | 78° | 80° | 81° | |||
| Missile details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Range (m) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (kg) |
Ricochet | ||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| 9M119 | ATGM | 445 | 4,000 | 16.5 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 5.72 | 80° | 82° | 90° | ||
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 41 (+4) | 34 (+11) | 22 (+23) | 0 (+45) | No |
Machine guns
The T-72B has access to a coaxial PKT 7.62 mm machine gun and a 12.7 mm NSVT anti-aircraft machine gun, which is mounted above the commander's hatch. The PKT is rarely useful in top tier matches, but the NSVT can be quite useful. The NSVT has 29 mm of penetration, allowing it to damage some light vehicles like IFVs and enemy SPAA. Additionally it is useful to engage enemy helicopters when they come close. Machine guns can also be used to try and shoot down enemy ATGMs, but this is unreliable. They can also be used to shoot the ground in front of the tank for a quick smoke screen of sorts, confusing the enemy and blocking their view for a clean shot.
| 12.7 mm NSVT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Pintle | 300 (60) | 700 | -4°/+75° | ±180° |
| 7.62 mm PKT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaxial | 2,000 (250) | 700 | - | - |
Usage in battles
There are three main ways to use the T-72B: as a flanker, as a sniper, or as a frontline support tank.
Flanking
The T-72B performs awesomely as a flanker, especially with the new engine. In many maps, such as Berlin, Maginot Line or Mozdok, it will be one of the best playstyles. If APFSDS hasn't been researched yet, try to know the locations of your most common opponents' ammo racks (i.e. XM-1 (Chrysler)/(GM), T-72 TURMS and Leopards 1/2), and aim at them, since HEAT-FS doesn't feature great damage against composite armours. When facing multiple enemies, prioritise disabling them (destroying gun breech/barrel, knocking out gunner, etc.) so that they don't pose an immediate threat and you can destroy them later.
Sniping
This is another great performance of the T-72, as it has adequate shell velocity and penetration. HEAT-FS penetrates 550 mm of armour at any distance, and its muzzle speed is faster than most of other HEAT-FS shell you will meet. Also, the APFSDS performs excellently because of its extreme velocity (~1,760 m/s) and high penetration (425 mm). Try to keep a distance of at least 1 km and no more than 1.5 km when using HEAT, but the unlocking of sabot shells will increase your range almost indefinitely. Try to cover your lower glacis, as it is your only weakspot at range.
Frontline support
This playstyle is very risky, as your slow reverse speed will turn your tank into a coffin, but with access to the 3BM42 shot, it will become more viable. Do not, ever, do this alone. Always try to have at least two reliable teammates covering you. Your main goal in this playstyle is to cover offensives, and defend and attack bases. Cover weaker tanks by attracting fire and secure base capturers. In this mode, you should not focus on making experience for your own, like capturing bases, but to ensure the achievement of victory. This style will mostly take your tank as sacrifice, unless played very carefully and prudently, but victory multipliers will overcome your losses.
Enemies worth noting:
- XM-1 (Chrysler)/(GM): Avoid attempting combat with the 3BK18M HEATFS shells, despite their having thin composite armour
- AMX-30B2/AMX-30B2 BRENUS: DM23/33 have enough armour penetration to penetrate T-72 driver frontal plates, though all shells are effective against them in return.
- Leopard 2K: Turret mantlet is resistant to 3BK18M.
- AMX-40: Turret mantlet and lower frontal plate are highly resistant to 3BK18M.
- Strv 103: Depending on the hull angling, HEAT-FS rounds such as the 3BK18M might ricochet. APFSDS is recommended to be used when facing it frontally.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Excellent composite armour protection
- Turret cheeks will chew up modern-day tank shells, invulnerable even to the mighty DM53
- CONTACT-1 ERA coverage to front and sides, provides great protection against chemical shells (~400 mm)
- Powerful main armament with autoloader, 3BM42 round, and laser rangefinder
- Barrel launched ATGMs, without extra reload time
- ESS and smoke grenades
Cons:
- Extremely prone to gun breech disabling, as in all post-war T-series
- Very bad reverse speed (-4 km/h)
- Lack of thermals at rank VII
- ERA provides insignificant protection against kinetic shells (~5 mm)
- Side armour is so thin that can be penetrated basically at any angle, which will inevitably ammo-rack you
- Small crew count, cramped interior and large ammo rack mean low survivability
- Poor gun depression
History
The T-72 was one of the most famous and widely produced Soviet main battle tanks of the Cold War era. Originating as a modification of the T-64, the T-72 retained its predecessor's composite armour, 125 mm smoothbore cannon, and compact dimensions, all modern features for the time. But it was intended to be easier to produce and maintain than the complex and unreliable T-64. Instead of the T-64's opposed piston engine, which promised high power in a compact package but turned out to be a mechanical nightmare, the T-72 used a more traditional V-46 engine with larger dimensions. The engine compartment and suspension were redesigned to suit the new engine. The original T-64 "MZ" autoloader was replaced with the "AZ" autoloader, which stored ammunition in two horizontal trays. The T-72 began to equip standard tank divisions and motorized units while elite units retained the T-64. The combat capabilities of the initial T-72 were very close despite its origin as a somewhat simplified T-64, as the heavier weight was compensated for by the greater engine power. The T-64 tended to have more advanced optics and fire control systems over its service life, and the later T-80 had much superior mobility, but the simple cost effectiveness and reliability of the T-72 made it an excellent tank for widespread deployment and export. It remains in service worldwide in many different variants and has arguably been a more successful design than its ostensibly higher-tech relatives.
The T-72B variant first appeared in 1985. At this time, the preceding T-72A had shown its age. The newest NATO tanks had guns and ammunition capable of penetrating early Soviet composite armour and the T-72A's fire control system was lacking. The T-64B, introduced several years earlier, had improved armour and a new fire control system capable of supporting gun-launched ATGMs like the 9M112 "Kobra". The T-72B set out to meet these standards.
As part of the improvements, the protection was improved dramatically. The turret was constructed with high hardness steel and improved "Super Dolly Parton" composite armour that bulged the turret cheeks even further. The increased volume necessitated cuts underneath the turret cheeks/sides to allow the driver to open his hatch if the turret was rotated. The composite armour used polymer and steel NERA layers much like the Leopard 2 and M1 Abrams instead of the "Kvartz" ceramic filler used on earlier T-72As. This provided improved chemical protection on par with these two NATO MBTs and also easier serviceability: the NERA plates could be accessed and replaced in the field if damaged, whereas the sintered quartz blocks were cast with the turret in the factory and could not be repaired. Kinetic protection was increased to a reported figure of 550 mm RHA equivalent.
The hull composite armour was switched to a new 60-10-10-20-20-50 configuration: a 60 mm front plate, four high hardness plates of 10 mm and 20 mm thickness, and a 50 mm back plate. While this is technically spaced armour instead of composite armour, it offered significant improvements in kinetic protection over the older textolite composition. In fact, comparative testing of the T-72B's glacis armour and the T-80BV's configuration showed that it was immune to even overpressure shots using 3BM32 "Vant" depleted uranium APFSDS, which penetrated the T-80BV using standard charges. Chemical protection was also improved and the T-72B's upper glacis was capable of resisting HEAT-FS rounds, man-portable ATGMs, and older full-size ATGMs.
The armour upgrades played a large role in increasing the T-72B's weight to about 43 tons at combat weight compared to the T-72A's 41 tons. To cope with this, a V-84 engine producing 840 horsepower was installed. It was a close derivative of the V-46 and in theory should have been very easy to retrofit to existing T-72s. However, its increased power and heat generation required modifications to the T-72B design. An engineer recalled that the V-84 somehow developed less power than the V-46 when installed in the T-72A.
The T-72B received a new 1A40-1 sighting complex with a lead calculator, improved laser rangefinder, and support for 9M119 "Svir" gun-launched ATGMs through an improved night sight. The gunner could lase a moving target while looking down the sight and the system would calculate and display how many mils to lead by in a secondary eyepiece. From the gunner's view, the calculation result would be superimposed on the sight view. This made it easier for the tank to engage moving targets, which previously was unassisted on early T-72A models, but the system was not precise enough for reliable long distance shooting and lagged behind the M60A3's fire control system in ease of use.
Other minor changes included modifications to the autoloader to accommodate the Svir ATGMs and an improved 2E42-2 "Zhasmin" stabilizer system with an electric drive instead of hydraulics. The vehicle represented in War Thunder is equipped with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armour, which became standard for T-72Bs out of the factory. The turret ERA was no longer mounted on brackets as on the T-64B or T-72AV, instead being placed directly on the turret surface. This more haphazard arrangement increased the coverage of the ERA but slightly decreased effectiveness due to suboptimal sloping towards incoming fire. Still, a T-72B with Kontakt-1 was virtually immune to single-charge chemical munitions. Later production variants were capable of equipping improved Kontakt-5 ERA, which in turn made them resistant to even the best NATO APFSDS rounds at the time.
The T-72B successfully addressed the immediate problems facing the T-72A. The protection now matched or exceeded the new NATO MBTs that were capable of dispatching the previous model and the fire control upgrades provided a welcome increase in offensive capabilities. This was achieved without sacrificing ease of production and the T-72B was widely produced and exported like prior models. No improvements were made to its mobility, which was now exceeded by the Abrams and Leopard 2, and the fire control system was still inferior to Western tanks. Still, it provided a solid foundation for modernizations like the T-72B3 and will likely stay in service for the next few decades. The famous T-90 had its beginnings as an upgraded "T-72BU" as well.
The T-72B did not see any combat with the Soviet Union. The succeeding Russian Federation has used the T-72B in Chechenya, Georgia, and elsewhere. Other customers and current users of the T-72B include Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Laos, Morocco, and Syria.
Devblog
By the middle of the 1980s, there was an objective need to upgrade the main battle tank of the Soviet Union - T-72 to modern battle performance values. The fact is that the vehicle seriously lacked firepower and modern fire control systems and its protection which wasn't bad at the time of conception, became obsolete due to the emergence of new powerful weapons. The big tank modernization program implied a comprehensive improvement of the T-72 in all its key characteristics.
In the early 80s, the guided weapon system under the name "Svir" was developed for the Soviet tanks with the ability to guide the missile via beam and launching it through the gun barrel. At the same time there was also work on development of the first generation of the "Contact-1" explosive reactive armour. Both of these novelties were in demand for the modernization of the T-72. The vehicle received a new combined hull armour pack for the upper frontal part which increases in size and its composition has been redistributed toward more steel. Also a new custom turret with larger dimensions has been installed, featuring new armour filler packs.
Due to an increased weight, the tank required a new engine which allowed it to maintain the good running characteristics of the base model. The upgraded version received the designation T-72B and was adopted in December 1984. This modification became the basis for a large number of versions and upgrades which made the T-72 the most mass produced 2nd generation MBT in the world. As an upgraded version this tank continues to serve in the Russian army and many other countries.
Media
- Skins
- Images
- Videos
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
| Ural Railroad Car Plant (УралВагонЗавод) | |
|---|---|
| Main Battle Tanks | |
| T-55 | T-55A · T-55AM-1 |
| T-62 | T-62 · T-62M-1 |
| T-72 | T-72A · T-72B · T-72B (1989) · T-72B3 |
| T-90 | Т-90А |
| Heavy Tanks | IS-6 |
| Tank Destroyers | SU-122-54 · IT-1 |
| Export/Captured | |
| MBTs | Type 59 · Т-62 №545 · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · ◊T-72M1 |
| See Also | Morozov Design Bureau |
| USSR medium tanks | |
|---|---|
| T-28 | T-28 (1938) · T-28 · T-28E |
| T-34-76 | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1940) · T-34 (1941) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34 (1942) · T-34E STZ · T-34E |
| T-34-57 | T-34-57 · T-34-57 (1943) |
| T-34-85 | T-34-85 (D-5T) · T-34-85 · T-34-85E |
| T-34-100 | T-34-100 |
| T-44 | T-44 · T-44-100 · T-44-122 |
| T-54 | T-54 (1947) · T-54 (1949) · T-54 (1951) |
| T-55 | TO-55 · T-55A · T-55AM-1 · T-55AMD-1 |
| T-62 | T-62 · T-62M-1 |
| T-64 | Object 435 · T-64A (1971) · T-64B |
| T-72 | T-72A · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-72B · T-72B (1989) · T-72B3 · T-72M2 Moderna |
| T-80 | T-80B · T-80U · T-80UD · T-80UK · T-80UM2 · Т-80U-Е1 · T-80BVM · Object 292 |
| T-90 | Т-90А · T-90M |
| Trophies/Lend-Lease | |
| Germany | ▂T-III · ▂T-V |
| Great Britain | ▂МК-IX "Valentine" |
| USA | ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 |











