Difference between revisions of "Kh-66"
(→General info: add table) |
(Edits) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | <!-- ''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.'' --> | ||
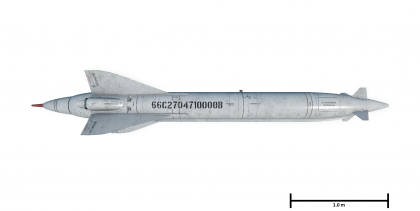
[[File:WeaponImage Kh-66.png|thumb|left|420px|The Kh-66 missile (scale is approximate)]] | [[File:WeaponImage Kh-66.png|thumb|left|420px|The Kh-66 missile (scale is approximate)]] | ||
{{Break}} | {{Break}} | ||
| − | + | The '''{{PAGENAME}}''' is a Soviet SACLOS-guided air-to-ground missile. It was introduced during [[Update "Hot Tracks"]]. | |
| − | The ''' | ||
=== Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | === Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* {{Specs-Link|mig-21_pfm}} | * {{Specs-Link|mig-21_pfm}} | ||
| − | == General info == | + | == General info == |
| − | <!--''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the missile.''--> | + | <!-- ''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the missile.'' --> |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
! colspan="2" | Missile characteristics | ! colspan="2" | Missile characteristics | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| '''Mass''' || 278 kg | | '''Mass''' || 278 kg | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | '''Guidance''' || Semi- | + | | '''Guidance''' || Semi-automatic (SACLOS) |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Maximum speed''' || 2 M | | '''Maximum speed''' || 2 M | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| '''Explosive mass''' || 65.28 kg TNTeq | | '''Explosive mass''' || 65.28 kg TNTeq | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | '''Armour penetration''' || | + | | '''Armour penetration''' || 74 mm |
| − | |} | + | |- |
| + | |} | ||
=== Effective damage === | === Effective damage === | ||
| − | ''Describe the type of damage produced by this type of missile (high explosive, splash damage, etc)'' | + | <!-- ''Describe the type of damage produced by this type of missile (high explosive, splash damage, etc)'' --> |
| + | A direct hit is almost always guaranteed to cripple if not outright destroy an enemy tank. It is also able to destroy lightly and even medium-armoured targets with proximity impact. | ||
=== Comparison with analogues === | === Comparison with analogues === | ||
| − | ''Give a comparative description of missiles that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' | + | <!-- ''Give a comparative description of missiles that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' --> |
| − | - | + | * [[AGM-12B Bullpup]] - It has a shorter range than the Kh-66, a flight speed 4 times slower, and a slightly lighter warhead. Jets can carry 4 to 5 AGM-12B missiles against only 2 for the Kh-66. |
| + | * [[AGM-12C Bullpup]] - It has an extra 6 km range over the Kh-66 but a flight speed 4 times slower. It is three times heavier than the Kh-66 and its warhead is twice larger than the Kh-66's. Like the Kh-66, jets can carry only 2 x AGM-12C. | ||
| + | * [[AS-20 Nord]] - It has a shorter range than the Kh-66, a slightly slower flight speed, and a warhead 4 times lighter. It is manually guided (WASD keys), which is less practical than mouse-aimed missiles. | ||
== Usage in battles == | == Usage in battles == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 46: | ||
=== Pros and cons === | === Pros and cons === | ||
| − | ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' | + | <!-- ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' --> |
'''Pros:''' | '''Pros:''' | ||
| − | * | + | * Great range, greater than most AA missiles |
* High explosive mass | * High explosive mass | ||
| Line 56: | Line 60: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' | + | <!-- ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' --> |
| + | The Kh-66 is an early version of the Kh-23 Grom air-to-ground missile. The missile was developed from the existing K-5 and K-8 (RS-2-US) beam-riding air-to-air missiles. Just before the war in Vietnam, the United States began fielding new guided missiles; most notably the AGM-12 Bullpup, which caused the Soviet Ministry of Aircraft Industry to request an air-to-ground version of earlier RS-2-US beam riding air-to-air missile.<ref>Friedman, Norman (1997), ''The Naval Institute Guide to World Naval Weapons Systems'', Naval Institute Press, p. 235, ISBN 978-1-55750-268-1</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This new missile was designated Kh-66 (as the year it entered design/testing was 1966) and began to be used on the MiG-21PFM airframe (itself a testbed aircraft designed in conjunction with the Kh-66). Later in 1968, the missile finally entered service. The weapon was an amalgamation of the K-5 and K-8's guidance and propulsion systems and had an increased warhead for better performance against ground and sea-based targets. While the missile performed at the required specifications set by the Soviet government, the weapon was only a stopgap measure until more suitable armaments were developed. This was due to the flaws in utilizing the weapon as the pilot had to dive towards his target and maintain a lock with the gunsight. The missile was further developed into the Kh-23 by Korolyov again in early 1968 with the intention of making the weapon more effective. With this, the Kh-66 was effectively put out of production for new models by 1973.<ref>https://web.archive.org/web/20110727014325/http://eng.ktrv.ru/docs/history_eng.doc ''History of JSC Tactical Missile Corporation'', pp. 3–4, archived from http://eng.ktrv.ru/docs/history_eng.doc (Word 97 DOC) on 2011-07-27, retrieved 2009-02-15</ref> | ||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| Line 62: | Line 69: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| − | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | + | <!-- ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' --> |
| − | * | + | ;Related development |
| − | * | + | * [[Kh-23M]] |
| + | * [[Kh-25ML]] | ||
| + | * [[Kh-29T]] | ||
| + | * [[Kh-29L]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Weapons of comparable role, configuration, and era | ||
| + | * [[AGM-12B Bullpup]] | ||
| + | * [[AGM-12C Bullpup]] | ||
| + | * [[AS-20 Nord]] | ||
| + | * [[AS-30 Nord]] | ||
| + | * [[Rb05A]] | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | + | <!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' |
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
| − | * ''other literature.'' | + | * ''other literature.'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | === References === | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
{{Missiles}} | {{Missiles}} | ||
[[Category:Suspended armaments]] | [[Category:Suspended armaments]] | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:40, 26 August 2022
Contents
Description
The Kh-66 is a Soviet SACLOS-guided air-to-ground missile. It was introduced during Update "Hot Tracks".
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
General info
| Missile characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Mass | 278 kg |
| Guidance | Semi-automatic (SACLOS) |
| Maximum speed | 2 M |
| Missile guidance time | 25 secs |
| Firing range | 10 km |
| Explosive mass | 65.28 kg TNTeq |
| Armour penetration | 74 mm |
Effective damage
A direct hit is almost always guaranteed to cripple if not outright destroy an enemy tank. It is also able to destroy lightly and even medium-armoured targets with proximity impact.
Comparison with analogues
- AGM-12B Bullpup - It has a shorter range than the Kh-66, a flight speed 4 times slower, and a slightly lighter warhead. Jets can carry 4 to 5 AGM-12B missiles against only 2 for the Kh-66.
- AGM-12C Bullpup - It has an extra 6 km range over the Kh-66 but a flight speed 4 times slower. It is three times heavier than the Kh-66 and its warhead is twice larger than the Kh-66's. Like the Kh-66, jets can carry only 2 x AGM-12C.
- AS-20 Nord - It has a shorter range than the Kh-66, a slightly slower flight speed, and a warhead 4 times lighter. It is manually guided (WASD keys), which is less practical than mouse-aimed missiles.
Usage in battles
The Kh-66 is used to perform Close Air Support from outside enemy AA effective range.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Great range, greater than most AA missiles
- High explosive mass
Cons:
- Hard to aim
- Only two missiles
- Heavy weight impacts flight performance
History
The Kh-66 is an early version of the Kh-23 Grom air-to-ground missile. The missile was developed from the existing K-5 and K-8 (RS-2-US) beam-riding air-to-air missiles. Just before the war in Vietnam, the United States began fielding new guided missiles; most notably the AGM-12 Bullpup, which caused the Soviet Ministry of Aircraft Industry to request an air-to-ground version of earlier RS-2-US beam riding air-to-air missile.[1]
This new missile was designated Kh-66 (as the year it entered design/testing was 1966) and began to be used on the MiG-21PFM airframe (itself a testbed aircraft designed in conjunction with the Kh-66). Later in 1968, the missile finally entered service. The weapon was an amalgamation of the K-5 and K-8's guidance and propulsion systems and had an increased warhead for better performance against ground and sea-based targets. While the missile performed at the required specifications set by the Soviet government, the weapon was only a stopgap measure until more suitable armaments were developed. This was due to the flaws in utilizing the weapon as the pilot had to dive towards his target and maintain a lock with the gunsight. The missile was further developed into the Kh-23 by Korolyov again in early 1968 with the intention of making the weapon more effective. With this, the Kh-66 was effectively put out of production for new models by 1973.[2]
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
- Related development
- Weapons of comparable role, configuration, and era
External links
References
- ↑ Friedman, Norman (1997), The Naval Institute Guide to World Naval Weapons Systems, Naval Institute Press, p. 235, ISBN 978-1-55750-268-1
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20110727014325/http://eng.ktrv.ru/docs/history_eng.doc History of JSC Tactical Missile Corporation, pp. 3–4, archived from http://eng.ktrv.ru/docs/history_eng.doc (Word 97 DOC) on 2011-07-27, retrieved 2009-02-15