HOT-3
Contents
Description
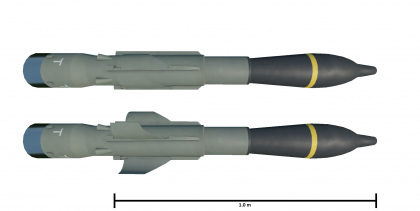
The HOT-3 is a Franco-German SACLOS-guided air-to-ground missile. It was introduced in Update 1.91 "Night Vision".
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
General info
The HOT-3 (also known as Haut subsonique Optiquement Téléguidé Tiré d'un Tube in French) is a second generation long-range anti-tank missile system that was developed originally as an effort to meet a joint requirement from both French and German armies by the German firm Bölkow and the French firm Nord-Aviation, to replace the existing SS.11 wire guided missiles that were used by both nations.
Bölkow merged later into MBB (Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm) while Nord-Aviation merged into Aérospatiale. They then formed Euromissile to design and produce the MILAN, Roland and HOT.
The HOT missiles become one of the most successful of its class, with thousands of missiles produced, used by no less than a dozen countries. The HOT missile system is commonly mounted on helicopters, such as the EC-665 Tiger HAD, or light vehicles.
The HOT-3 missile is an anti-tank guided missile capable of penetrating up to 1,250 mm, with a TNT equivalent of 4,920 g. The missile moves roughly at 240 m/s, and it is using the SACLOS (mouse based) guidance system. Multiple variants of the HOT missiles were developed.
After traveling a set distance, the HOT missile deploys its fins for added stabilization. This makes the missile very accurate and in case of a lost lock or an user error, the missile can be quickly set to the correct path once again with no real issues.
| Missile characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Mass | 23.6 kg |
| Guidance | Semi-automatic (SACLOS) |
| Maximum speed | 250 m/s |
| Firing range | 4.3 km |
| Missile guidance time | 19 secs |
| Explosive mass | 6.46 kg TNTeq |
| Armour penetration | 1,250 mm |
Comparison of HOT variants
| Name | Length (mm) |
Wingspan (mm) |
Diameter (mm) |
Weight at launch (kg) |
Type of warhead | Penetration power (mm) |
Range (m) |
Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOT | 1,270 | 310 | 136 | 23.5 | 5 kg HEAT | 800 | 75 - 4,000 | 240 |
| HOT-2MP / HOT-2 | 1,300 | 310 | 150 | 23.5 | 5 kg HEAT | 350 (-2MP) / 900 (-2) | 75 - 4,000 | 240 |
| HOT-3 | 1,300 | 310 | 150 | 24.5 | 6.48 kg tandem HEAT | 1,250 | 75 - 4,300 | 240 |
Effective damage
The HOT-3 missile has massive amount of penetration but it does not create enough spalling to one hit kill reliably, mainly if attacking the frontal armour of hostile tanks. It creates little to no splash damage so accuracy is required or otherwise, no damage will be dealt and the target may escape or even try to shoot the user down.
Comparison with analogues
| Comparable missiles to the HOT-3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Year of Production | Velocity (m/s) | Maximum Penetration (mm) |
| SS.11 | 1956 | 190 | 600 |
| 9M120 Ataka | 1980s | 550 | 800 |
Usage in battles
As with other helicopter mounted ATGMs, it is best to stay out of combat and hover above a hill or near some cover that you can retreat to in case an AA starts shooting at you. There are two main ways of using the HOT-3 ATGMs, both of which require fine degree of awareness and also map knowledge, so do not give up if you are new to modern helicopter systems.
Direct
The first way of using the HOT-3 is to rush as fast as you can towards the frontline while also taking note of any hills or obstacles that could be used as cover. If you have reached a point where most of your targets are in your effective range of your HOT-3 (this being under 4.3 km; the user can use the radar lock function as a makeshift rangefinder), you should try to find a spot where you can easily retreat to, like for example a hill as mentioned above. Since the velocity of the missile isn't anything to brag about, being only about 240 m/s, and that you have to manually track it without breaking line of sight, makes it quite cumbersome to use but nonetheless still effective at dispatching enemy armour. Before engaging, always scan the surrounding area as you may never know if an AA is looking at you.
Flanking
The second way of using the HOT-3 is to flank the sides of the map, preferably the side which has hills or plenty of cover to hide behind, while also being far so that the enemy does not hear your engine. Once you have infiltrated the sides or the rear of the enemy, and you have found some cover to hide behind, you can now start engaging hostile targets. Always prioritize AA over anything, as they are the bane of any helicopter's existence. If you run out of your HOT-3 missiles, go back the way you came and land on your heliport. Rearm your missiles and head back to combat once again.
Protection against aircraft
You may be wondering how you can protect against aircraft which can attack your helicopter at any angle. The truth is, you really cannot effectively engage aircraft with the HOT-3s. This does not mean however that it is impossible, since you can radar lock onto a jet. If it does not notice that it is being tracked by your missile and it isn't pulling any manoeuvres, the HOT-3 may just catch the jet and destroy it easily. This also applies to helicopters, but one shouldn't try to shoot down hostile aircraft or helicopters with HOT-3s as majority of times, the missile will be wasted. Treat it more as a "last resort" than an efficient aircraft killer.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- High penetration power (up to 1250 mm)
- Fairly long reach: 4,300 m range
- HOT-3s are fairly accurate
Cons:
- Rather low velocity of 240 m/s
- Bad post-penetration effects; creates below average spalling
- Guidance can be broken fairly easily if the user is not careful
History
By the year 1975, the development of the missiles was completed and the evaluations had been performed by various ministries of defense. The mass production of these missiles began in the year 1976 and the first HOT missiles were deployed into the field in 1978. A night sight to help with night operations called the Viviane, was developed in the early 1980s.
In the year 1985, the HOT-2 followed suite with a multipurpose warhead variant called the HOT-2MP entering service in 1992. While the HOT-2MP wasn't great at penetrating armour, it had fragmentation but also incendiary effects which proved to be adequate at dispatching infantry and soft targets. By the year 1987, 1,434 launchers and 70,350 missiles were produced.
In the year 1998, the HOT-3 was introduced, which has a tandem shaped-charge HEAT warhead capable of piercing trough reactive armour. A laser-proximity fuze located in the front half of the nose measures the distance between the target and the missile. If the correct range is achieved, a small nipple at the front of the nose containing a smaller HEAT charge is ejected forward from the missile body to pre-detonate the reactive armour followed by the detonation of main HEAT warhead. The missile itself also had its anti-jamming capabilities improved, and so it was selected to be used as the missile armament for the Tiger attack helicopters for France and Germany.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
- 9M120-1 Ataka - another SACLOS missile system similar to that of the HOT
- SS.11 - a missile system which the HOT missile was derived from and replaced
External links