F6F-5N
Contents
| This page is about the American naval fighter F6F-5N. For the French version, see F6F-5N (France). For other versions, see F6F (Family). |
Description
The F6F-5N Hellcat is a rank American naval fighter
with a battle rating of (AB), (RB), and (SB). It was introduced in Update 1.65 "Way of the Samurai".
General info
Flight performance
Describe how the aircraft behaves in the air. Speed, manoeuvrability, acceleration and allowable loads - these are the most important characteristics of the vehicle.
| Characteristics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock | |||||||
| Max Speed (km/h at 5,730 m) |
Max altitude (meters) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (meters/second) |
Take-off run (meters) | |||
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | ||
| 602 | 581 | 22.2 | 23.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 399 | |
| Upgraded | |||||||
| Max Speed (km/h at 5,730 m) |
Max altitude (meters) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (meters/second) |
Take-off run (meters) | |||
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | ||
| 661 | 629 | 19.8 | 21.0 | 16.7 | 11.8 | 399 | |
Details
| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ |
| Limits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wing-break speed (km/h) |
Gear limit (km/h) |
Combat flaps (km/h) |
Max Static G | |
| + | - | |||
| 803 | 510 | ~11 | ~4 | |
| Optimal velocities | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons (km/h) |
Rudder (km/h) |
Elevators (km/h) |
Radiator (km/h) |
| < 432 | < 420 | < 420 | > 420 |
| Compressor (RB/SB) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Setting 1 | ||
| Optimal altitude | 100% Engine power | WEP Engine power |
| 518 m | 2,000 hp | 2,398 hp |
| Setting 2 | ||
| Optimal altitude | 100% Engine power | WEP Engine power |
| 4,724 m | 1,800 hp | 2,158 hp |
| Setting 3 | ||
| Optimal altitude | 100% Engine power | WEP Engine power |
| 6,400 m | 1,650 hp | 1,978 hp |
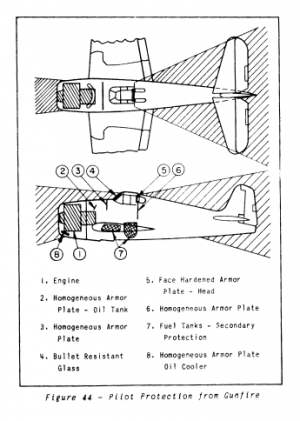
Survivability and armour
- 3 mm steel - below the engine and above cooling system
- 6.35 mm steel - behind the pilot
- 38 mm bulletproof glass - armoured windscreen
Armaments
Offensive armament
The F6F-5N is armed with:
- 2 x 20 mm AN/M2 cannons, wing-mounted (231 rpg = 462 total)
- 4 x 12.7 mm Browning M2 machine guns, wing-mounted (400 rpg = 1,600 total)
Suspended armament
The F6F-5N can be outfitted with the following ordnance:
- Without load
- 6 x HVAR rockets
- 2 x Tiny Tim rockets
- 2 x 1,000 lb AN-M65A1 bombs (2,000 lb total)
- 2 x 1,000 lb AN-M65A1 bombs + 6 x HVAR rockets (2,000 lb total)
- 1 x Mk.13/44 torpedo
Usage in battles
The F6F-5N was a versatile fighter during World War II and it proves this with both the capabilities of the airframe along with the varied ordnance it can carry. The powerful weapons that the F6F-5N has on-board can make short work of enemy aircraft and some ground targets, and the sizable amount of suspended weapons allows the aircraft to be used in support roles when attacking critical ground targets. In addition, employment of the radar can make the F6F-5N a deadly fighter in night combat or in adverse weather conditions.
Aerial combat
This F6F-5N has a powerful engine and a relatively heavy airframe, which allows it to perform well in diving and manoeuvering attacks. Against aircraft that are less manoeuverable or are unable to maintain speed during combat the F6F-5N can easily take them out. When fighting lighter and more nimble enemies, it pays to be cautious and not commit into a fight without having superior energy to escape if it becomes necessary.
During the night, the radar becomes and invaluable tool to seek out and destroy enemy aircraft. It is best to position the aircraft where targets can be detected from the side or rear aspect which allows the F6F-5N to follow them and shoot them down. Take note of the limited range of the radar and that targets may only be visible up to a few kilometers away. A helpful range setting for the radar is the 9.25 km (5.75 mi) scan distance, as further options can make it difficult to properly find and chase down targets. When moving in closer, switching to the 1.85 km (1.15 mi) scan distance can make it easier to stay on a target from behind as well as transition to the radar track mode.
Ground attack
The F6F-5N is effective in ground attack where it can be outfitted with either bombs or rockets. The 1,000 lb bombs have a devastating effect on ships and hardened structures, and especially on vehicles which are clustered in a compact area. The agility of the aircraft makes it ideal to outfit rockets, which can be dropped if not needed. The larger Tiny Tim rockets will pack a huge punch against heavily armoured vehicles or static defenses (such as heavy tanks or pillboxes) and ships. The Tiny Tims can even be used to finish off an enemy base that has very little health remaining. HVAR rockets work best when reserved for lighter armoured vehicles some hardened concrete structures and bombers.
Naval attack
Although the bombs and rockets that the F6F-5N can carry are able to be used against naval targets, they can place the aircraft into dangerous situations when attacking ships. The F6F-5N can carry a single Mk.13/44 torpedo which will prove deadly against any naval enemy. Using it effectively requires planning ahead of time, as simply charging straight at a ship will likely end up in a lost aircraft. Working around terrain such as islands and hills to sneak in close and dropping the torpedo at the latest possible time can result in a sunken ship and a living aircraft.
Radars
The F6F-5N is equipped with an AN/APS-6 search and tracking radar. The radar is mounted in a pod under the right wing tip.
| AN/APS-6 - Target Detection Radar | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Detection Range |
Guaranteed Detection Range |
Max Azimuth Scan Angle |
Max Elevation Scan Angle |
| 60,000 m (theoretical) |
7,200 m | ±60° | ±60° |
| AN/APS-6 - Target Tracking Radar | |||
| Maximum Tracking Range |
Minimum Tracking Range |
Azimuth Tracking Angle |
Elevation Tracking Angle |
| 1,000 m | 150 m | ±15° | ±15° |
Manual Engine Control
| MEC elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixer | Pitch | Radiator | Supercharger | Turbocharger | ||
| Oil | Water | Type | ||||
| Not controllable | Controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Not auto controlled |
Separate | Controllable 3 gears |
Not controllable |
Modules
| Tier | Flight performance | Survivability | Weaponry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Fuselage repair | Radiator | Offensive 12 mm | ITC mk.III | |
| II | Compressor | Airframe | New 12 mm MGs | FRC mk.2 | |
| III | Wings repair | Engine | Offensive 20 mm | LFRC mk.12 | |
| IV | Engine injection | Cover | New 20 mm cannons | FLBC mk.1 | |
Payload modules unlock the following:
- ITC mk.III: One torpedo
- FRC mk.2: Six HVAR rockets
- LFRC mk.12: Two Tiny Tims
- FLBC mk.1: Two 1,000 lb AN-M65A1 bombs
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Cannon armament
- Great variety of weapons for any map, aerial combat, ground attack and maps with naval ships
- Decent climb rate and manoeuverability
- Has a search and tracking radar
- Capable of operating from an aircraft carrier
Cons:
- Slower than the standard F6F-5
- Not as energy-efficient in a climb as other American aircraft (such as the P-47)
- Overall worse performance than F6F
History
The F6F-5N was a modification of the standard F6F-5 for use as a night fighter. These aircraft were fitted with additional equipment in the form of a radio altimeter and radar. The Westinghouse AN/APS-6 radar was installed on the starboard wing of the F6F-5N, with units being completed in middle and late 1944. The APS-6 served as a method to search and destroy hostile aircraft in conditions with zero visibility, with data being displayed in a standard B-scope view of the target azimuth on the x-axis and target range on the y-axis. Aside from target search and tracking, the APS-6 could also be used in a navigation role by tracking a radar emitter or beacon with a search range of up to 100 miles.[1] Due to the simplifications from the earlier AN/APS-4 radar, the APS-6 was small enough to be installed in single-engine aircraft which allowed for independent action among night fighters. Another feature of the F6F-5N was the Type GR-1 automatic pilot, which gave pilots the ability to maintain a stable flight attitude with minimal input. Just as with the F6F-5, the -5N used the Pratt & Whitney R-2800-10W and had provisions to used a mixed armament of 2x 20 mm M2 cannons and 4x .50 cal Browning machine guns. The F6F-5N is noted as being one of the better American night fighters during World War II and was chosen to be a night fighter over other aircraft such as the F4U Corsair.[1]
Media
-
 An underside view of a F6F-5N carrying two Tiny Tim rockets. These rockets had to be released before igniting so to clear the propeller arc.
An underside view of a F6F-5N carrying two Tiny Tim rockets. These rockets had to be released before igniting so to clear the propeller arc. -
 A view of a F6F-5N firing off a Tiny Tim rocket at an enemy target.
A view of a F6F-5N firing off a Tiny Tim rocket at an enemy target. -
 A side view of the shackle connection of the Tiny Tim rocket to the external pylon of the F6F-5N.
A side view of the shackle connection of the Tiny Tim rocket to the external pylon of the F6F-5N.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the aircraft;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
- AviationShoppe link for Grumman F6F Hellcat Pilot's Manual
- Ibiblio HyperWar link for "The AN/APS-6 Aircraft Radar"
References
| Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation | |
|---|---|
| Aircraft | |
| Fighters | |
| F3F | F3F-2 · Galer's F3F-2 |
| F4F Wildcat | F4F-3 · F4F-4 |
| XF5F Skyrocket | XF5F · XP-50 |
| F6F Hellcat | F6F-5 · F6F-5N |
| F7F Tigercat | F7F-1 · F7F-3 |
| F8F Bearcat | F8F-1 · F8F-1B |
| Jet Fighters | |
| F9F Panther/Cougar | F9F-2 · F9F-5 · F9F-8 |
| F-11 Tiger | F11F-1 |
| F-14 Tomcat | F-14A Early · F-14B |
| Jet Strike Aircraft | |
| A-6 Intruder | A-6E TRAM |
| Bombers | TBF-1C |
| Export | ▄Martlet Mk IV · ▄F6F-5 · ▄F6F-5N · ▄F8F-1B · ▄Avenger Mk II · ▄Hellcat Mk II |
| ▄F-14A IRIAF | |
| Naval Vehicles | |
| Patrol Gunboat Hydrofoil (PGH) | USS Flagstaff |
| USA fighters | |
|---|---|
| P-26 Peashooter | P-26A-33 · P-26A-34 · P-26A-34 M2 · P-26B-35 |
| P-36 Hawk | P-36A · Rasmussen's P-36A · P-36C · ○P-36C · P-36G |
| P-39 Airacobra | P-400 · P-39N-0 · P-39Q-5 |
| P-40 | P-40C · P-40E-1 · P-40E-1 TD · P-40F-10 |
| P-43 Lancer | P-43A-1 |
| P-47 Thunderbolt | P-47D-22-RE · P-47D-25 · P-47D-28 · P-47M-1-RE · ⋠P-47M-1-RE · P-47N-15 |
| P-51 Mustang | P-51 · P-51A (Thunder League) · P-51C-10 · P-51D-5 · P-51D-10 · P-51D-20-NA · P-51D-30 · P-51H-5-NA |
| P-63 Kingcobra | P-63A-5 · P-63A-10 · P-63C-5 · ␠Kingcobra |
| Prototypes | XP-55 |
| F2A Buffalo | F2A-1 · Thach's F2A-1 · F2A-3 |
| BF2C | BF2C-1 |
| F3F | F3F-2 · Galer's F3F-2 |
| F4F Wildcat | F4F-3 · F4F-4 |
| F4U Corsair | F4U-1A · F4U-1A (USMC) · F4U-1D · F4U-1C · F4U-4 · F4U-4B · F4U-4B VMF-214 · F2G-1 |
| F6F Hellcat | F6F-5 · F6F-5N |
| F8F Bearcat | F8F-1 · F8F-1B |
| Other countries | ▃Ki-43-II · ▃Ki-61-Ib · ▃A6M2 · ▃Bf 109 F-4 · ▃Fw 190 A-8 · ▃Spitfire LF Mk IXc |