Difference between revisions of "Po-2M"
U123967134 (talk | contribs) (→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
(→Suspended armament: Edits) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
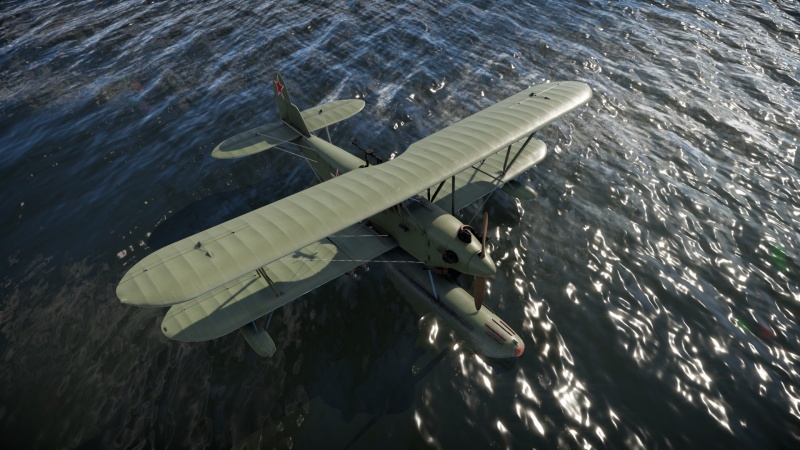
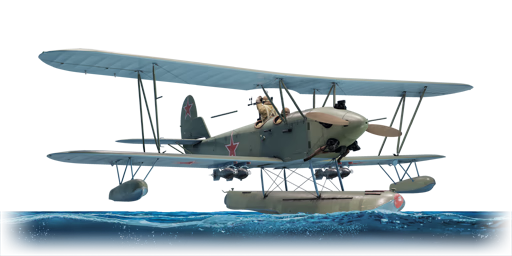
The '''{{Specs|name}}''' (or Po-2P) was a proposed Soviet biplane intended to be used as a floatplane version of the [[Po-2]]. It was developed in the 1940s and was successfully tested at the Khimki water reservoir near Moscow. Due to the requirement to mount a bomb load beneath the lower wings, it was created using a single-float scheme. Apart from that, there were only a few minor differences between it and the land-based version, such as the addition of a spinner to the propeller, hiding the rudder control cables in the fuselage, and a trimming glacis to the elevator. Despite positive test results, it was never put into production. It's very likely that biplane designs were simply considered out of favour at the time, and thus the aircraft never stood a chance. | The '''{{Specs|name}}''' (or Po-2P) was a proposed Soviet biplane intended to be used as a floatplane version of the [[Po-2]]. It was developed in the 1940s and was successfully tested at the Khimki water reservoir near Moscow. Due to the requirement to mount a bomb load beneath the lower wings, it was created using a single-float scheme. Apart from that, there were only a few minor differences between it and the land-based version, such as the addition of a spinner to the propeller, hiding the rudder control cables in the fuselage, and a trimming glacis to the elevator. Despite positive test results, it was never put into production. It's very likely that biplane designs were simply considered out of favour at the time, and thus the aircraft never stood a chance. | ||
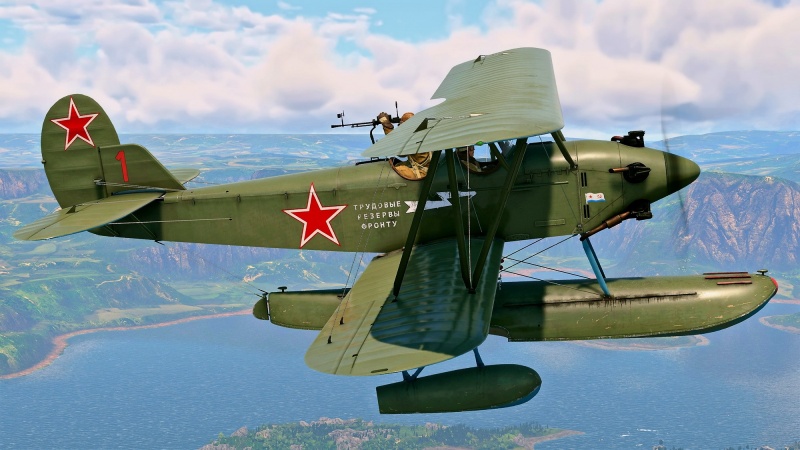
| − | The {{Specs|name}} was introduced during [[Update "Drone Age"]] as a reward for the 2022 [[wt:en/news/7882-event-project-overpowered-en|Project "Overpowered"]] event. It essentially plays the same as the Po-2 | + | The {{Specs|name}} was introduced during [[Update "Drone Age"]] as a reward for the 2022 [[wt:en/news/7882-event-project-overpowered-en|Project "Overpowered"]] event. It essentially plays the same as the Po-2 but with some minor improvements. Unfortunately, its status as the slowest plane in the game remains unchanged, but its payload options remain impressive. In comparison to the Po-2, it trades two 50 kg bombs for the ability to carry four more rockets of each type, and even incendiary bombs. The defensive machine gun was also changed to a [[DA (7.62 mm)|7.62 mm DA]]. |
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
{{Specs-Avia-Suspended}} | {{Specs-Avia-Suspended}} | ||
<!-- ''Describe the aircraft's suspended armament: additional cannons under the wings, bombs, rockets and torpedoes. This section is especially important for bombers and attackers. If there is no suspended weaponry remove this subsection.'' --> | <!-- ''Describe the aircraft's suspended armament: additional cannons under the wings, bombs, rockets and torpedoes. This section is especially important for bombers and attackers. If there is no suspended weaponry remove this subsection.'' --> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '' | + | The '''''{{PAGENAME}}''''' can be outfitted with the following ordnance: |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="100%" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! !! width="7%" | 1 !! width="7%" | 2 !! width="7%" | 3 !! width="7%" | 4 !! width="7%" | 5 !! width="7%" | 6 | ||
| + | | rowspan="8" width="30%" | <div class="ttx-image">[[File:Hardpoints_{{PAGENAME}}.png]]</div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[FAB-50sv (50 kg)|50 kg FAB-50sv]] bombs | ||
| + | | || 1 || 1 || 1 || 1 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[FAB-100sv (100 kg)|100 kg FAB-100sv]] bombs | ||
| + | | || || 1 || 1 || || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[ZAB-50FP incendiary]] bombs | ||
| + | | || 1 || 1 || 1 || 1 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[RBS-82]] rockets | ||
| + | | 4 || || || || || 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[ROS-82]] rockets | ||
| + | | 4 || || || || || 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[ROS-132]] rockets | ||
| + | | 4 || || || || || 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="7" | Maximum permissible weight imbalance: 100 kg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="8" | * Bombs and rockets cannot be equipped simultaneously | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Navigation-Start|Default weapon presets}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-First-Simple-Line}} | ||
| + | * 4 x 50 kg FAB-50sv bombs (200 kg total) | ||
| + | * 2 x 100 kg FAB-100sv bombs (200 kg total) | ||
| + | * 4 x ZAB-50FP incendiary bombs | ||
| + | * 8 x ROS-82 rockets | ||
| + | * 8 x RBS-82 rockets | ||
| + | * 8 x ROS-132 rockets | ||
| + | {{Navigation-End}} | ||
=== Defensive armament === | === Defensive armament === | ||
| Line 117: | Line 153: | ||
** Access to incendiary bombs at reserve BR | ** Access to incendiary bombs at reserve BR | ||
** Rockets are effective against ground targets | ** Rockets are effective against ground targets | ||
| + | * Can destroy up to 4 bases in realistic battles | ||
| + | * Able to land on water | ||
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| − | * | + | * Its slow speed makes it an easy target for fighters |
| − | |||
* Wing break speed is low | * Wing break speed is low | ||
* Lacks any offensive armament | * Lacks any offensive armament | ||
| + | * Low engine power | ||
| + | * Poor defensive armament | ||
| + | * Ineffective rudder making it hard to aim rockets | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | + | Early work on the U-2M, or Po-2M happened at Factory No 25 in Moscow under the supervision of Sergey Kocherigin. The Po-2M, at the time was designated MU-2 or U-2M, had one central floats, and 2 smaller secondary floats for lateral stability. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Tests of the Po-2M were conducted on the Moscow river in spring of 1931, where it was found the main disadvantage of the Po-2M was starting the engine. It was extremely uncomfortable to start the engine manually, because there was no other way of starting the engine at the time, while standing on one side of the floats. After the appearance of the Sh-2 flying boat, the USSR didn't have need for any more floatplanes. So the conversion of the U-2 ([[Po-2]]) into a floatplane was temporarily stopped. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The conversion continued nine years later, with the appearance of a more powerful M-11D engine with 127 HP and featured a pneumatic self-starter. At the same time, the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute conducted an extensive investigation into floats for aircraft of different gross weights, speeds and roles. For the U-2, they selected the Model 10 twin float design, as they were intended to have a high lift-drag ratio at low speeds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The single-float Po-2M that we know and love was made at factory No 51 under the supervision of Nikolai Polikarpov, while the dual float U-2M was made at factory No 23. Based on his wartime experience, Polikarpov decided to make a special-purpose combat aircraft to carry out military operations in area's that have lakes and rivers. So that the new float aircraft could put bombs under the wings, he chose a single float design with two secondary floats. Armament included 2 [[FAB-100sv (100 kg)|100 kg FAB-100sv]] bombs, 4 [[FAB-50sv (50 kg)|50 kg FAB-50sv]] bombs, 4 [[ZAB-50FP_incendiary|ZAB-50FP]] bombs, 8 rockets ([[ROS-132]], [[RBS-82]], and [[ROS-82]]), and a single rear-mounted [[DA (7.62 mm)|7.62 mm DA]] machine gun. A new NP-Po-2 Night bombing sight was used as well. | ||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| Line 140: | Line 185: | ||
* ''reference to the series of the aircraft;'' | * ''reference to the series of the aircraft;'' | ||
* ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' --> | * ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Related development | ||
* [[Po-2]] | * [[Po-2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Aircraft of a similar role, configuration or era | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[OS2U-1]] | ||
| + | * [[OS2U-3]] | ||
| + | * [[F1M2]] | ||
| + | * [[S17BS]] | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 17 November 2024
| This page is about the premium Soviet bomber Po-2M. For the gift version, see Po-2. For the race event version, see Po-2 Night Witch. |
Contents
Description
The Po-2M (or Po-2P) was a proposed Soviet biplane intended to be used as a floatplane version of the Po-2. It was developed in the 1940s and was successfully tested at the Khimki water reservoir near Moscow. Due to the requirement to mount a bomb load beneath the lower wings, it was created using a single-float scheme. Apart from that, there were only a few minor differences between it and the land-based version, such as the addition of a spinner to the propeller, hiding the rudder control cables in the fuselage, and a trimming glacis to the elevator. Despite positive test results, it was never put into production. It's very likely that biplane designs were simply considered out of favour at the time, and thus the aircraft never stood a chance.
The Po-2M was introduced during Update "Drone Age" as a reward for the 2022 Project "Overpowered" event. It essentially plays the same as the Po-2 but with some minor improvements. Unfortunately, its status as the slowest plane in the game remains unchanged, but its payload options remain impressive. In comparison to the Po-2, it trades two 50 kg bombs for the ability to carry four more rockets of each type, and even incendiary bombs. The defensive machine gun was also changed to a 7.62 mm DA.
General info
Flight performance
| Characteristics | Max speed (km/h at 0 m - sea level) |
Max altitude (metres) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (metres/second) |
Take-off run (metres) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||
| Stock | 130 | 126 | 30.6 | 31.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 258 | |
| Upgraded | 139 | 134 | 29.5 | 30.0 | 2.8 | 2.3 | ||
Details
| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| X | X | X | X | X |
| Limits | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wings (km/h) | Gear (km/h) | Flaps (km/h) | Max Static G | |||
| Combat | Take-off | Landing | + | - | ||
| 190 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ~5 | ~3 | |
| Optimal velocities (km/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons | Rudder | Elevators | Radiator |
| < 200 | < 200 | < 200 | > 295 |
Survivability and armour
Examine the survivability of the aircraft. Note how vulnerable the structure is and how secure the pilot is, whether the fuel tanks are armoured, etc. Describe the armour, if there is any, and also mention the vulnerability of other critical aircraft systems.
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Suspended armament
The Po-2M can be outfitted with the following ordnance:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kg FAB-50sv bombs | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 100 kg FAB-100sv bombs | 1 | 1 | |||||
| ZAB-50FP incendiary bombs | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| RBS-82 rockets | 4 | 4 | |||||
| ROS-82 rockets | 4 | 4 | |||||
| ROS-132 rockets | 4 | 4 | |||||
| Maximum permissible weight imbalance: 100 kg | |||||||
| * Bombs and rockets cannot be equipped simultaneously | |||||||
| Default weapon presets | |
|---|---|
| |
Defensive armament
The Po-2M is defended by:
- 1 x 7.62 mm DA machine gun, dorsal turret (315 rpg)
Usage in battles
Describe the tactics of playing in the aircraft, the features of using aircraft in a team and advice on tactics. Refrain from creating a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view, but instead, give the reader food for thought. Examine the most dangerous enemies and give recommendations on fighting them. If necessary, note the specifics of the game in different modes (AB, RB, SB).
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Various payload options
- Access to incendiary bombs at reserve BR
- Rockets are effective against ground targets
- Can destroy up to 4 bases in realistic battles
- Able to land on water
Cons:
- Its slow speed makes it an easy target for fighters
- Wing break speed is low
- Lacks any offensive armament
- Low engine power
- Poor defensive armament
- Ineffective rudder making it hard to aim rockets
History
Early work on the U-2M, or Po-2M happened at Factory No 25 in Moscow under the supervision of Sergey Kocherigin. The Po-2M, at the time was designated MU-2 or U-2M, had one central floats, and 2 smaller secondary floats for lateral stability.
Tests of the Po-2M were conducted on the Moscow river in spring of 1931, where it was found the main disadvantage of the Po-2M was starting the engine. It was extremely uncomfortable to start the engine manually, because there was no other way of starting the engine at the time, while standing on one side of the floats. After the appearance of the Sh-2 flying boat, the USSR didn't have need for any more floatplanes. So the conversion of the U-2 (Po-2) into a floatplane was temporarily stopped.
The conversion continued nine years later, with the appearance of a more powerful M-11D engine with 127 HP and featured a pneumatic self-starter. At the same time, the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute conducted an extensive investigation into floats for aircraft of different gross weights, speeds and roles. For the U-2, they selected the Model 10 twin float design, as they were intended to have a high lift-drag ratio at low speeds.
The single-float Po-2M that we know and love was made at factory No 51 under the supervision of Nikolai Polikarpov, while the dual float U-2M was made at factory No 23. Based on his wartime experience, Polikarpov decided to make a special-purpose combat aircraft to carry out military operations in area's that have lakes and rivers. So that the new float aircraft could put bombs under the wings, he chose a single float design with two secondary floats. Armament included 2 100 kg FAB-100sv bombs, 4 50 kg FAB-50sv bombs, 4 ZAB-50FP bombs, 8 rockets (ROS-132, RBS-82, and ROS-82), and a single rear-mounted 7.62 mm DA machine gun. A new NP-Po-2 Night bombing sight was used as well.
Media
- Skins
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of a similar role, configuration or era
External links
| Polikarpov Design Bureau (Опытное конструкторское бюро Поликарпова) | |
|---|---|
| I-15 | I-15 WR · I-15 M-22 · I-15 M-25 · I-15bis · Krasnolutsky's I-15bis |
| I-153 | I-153 M-62 · Zhukovsky's I-153-M62 · I-153P |
| I-16 | I-16 type 5 · I-16 type 10 · I-16 type 18 · I-16 type 24 · I-16 type 27 · I-16 type 28 |
| I-180 | I-180S · I-185 (M-71) · I-185 (M-82) |
| ITP | ITP (M-1) |
| Twin-engine fighters | TIS MA |
| Bombers | Po-2 · Po-2M |
| Export | ␗I-15bis · ␗I-153 M-62 · ␗I-16 type 5 · ␗I-16 type 10 · ␗I-16 type 17 · ␗I-16 Chung 28 |
| USSR bombers | |
|---|---|
| SB and Ar | SB 2M-100 · SB 2M-103 · SB 2M-103 MV-3 · SB 2M-103U · SB 2M-103U MV-3 · SB 2M-105 · Ar-2 |
| Yer-2 (petrol) | Yer-2 (M-105) · Yer-2 (M-105) TAT · Yer-2 (M-105R) TAT · Yer-2 (M-105R) LU |
| Yer-2 (diesel) | Yer-2 (ACh-30B) (e) · Yer-2 (ACh-30B) (l) |
| Tu | Tu-2 · Tu-2S · Tu-2S-44 · Tu-2S-59 · Tu-4 |
| Pe | Pe-2-1 · Pe-2-31 · Pe-2-83 · Pe-2-110 · Pe-2-205 · Pe-2-359 · Pe-8 |
| IL | DB-3B · IL-4 |
| Po | Po-2 · Po-2M |
| Other | MBR-2-M-34 · TB-3M-17-32 · Yak-4 · Be-6 |
| Lend-Lease | ▂PBY-5A Catalina · ▂Hampden TB Mk I · ▂A-20G-30 · ▂B-25J-30 |
| USSR premium aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Fighters | Krasnolutsky's I-15bis · I-16 type 28 · Zhukovsky's I-153-M62 · I-153P · I-180S · I-301 · ITP (M-1) |
| LaGG-3-4 · LaGG-3-23 · LaGG-3-34 · Dolgushin's La-7 · La-11 | |
| Eremin's Yak-3(e) · Yak-3 (VK-107) · Yak-3T · Golovachev's Yak-9M | |
| ▂P-39K-1 · ▂Pokryshkin's P-39N-0 · ▂P-39Q-15 · ▂P-40E-1 · ▂P-47D-27 · ▂P-63A-5 · ▂P-63A-10 · ▂P-63C-5 | |
| ▂Hurricane Mk IIB · ▂Spitfire Mk IXc · ▂Fw 190 D-9 | |
| Twin-engine fighters | I-29 |
| Jet fighters | Su-11 · MiG-15bis ISh · MiG-17AS · MiG-21S (R-13-300) · MiG-23ML |
| Strike aircraft | IL-2M "Avenger" · IL-2 M-82 · IL-8 (1944) · Su-6 · Tandem MAI · TIS MA · Su-8 · Tu-1 |
| Yak-38 · Su-7BMK · Su-25K · Su-39 | |
| Bombers | Po-2M · Be-6 · MBR-2-M-34 · Pe-2-205 · TB-3M-17-32 |
| ▂PBY-5A Catalina · ▂Hampden TB Mk I · ▂A-20G-30 · ▂B-25J-30 | |