Difference between revisions of "P-61C-1"
m (Updated external links format.) |
(Edits.) |
||
| Line 329: | Line 329: | ||
* ''other literature.'' --> | * ''other literature.'' --> | ||
| − | * [https://ia801208.us.archive.org/33/items/PilotTrainingManualForTheBlackWidowP61/PilotTrainingManualForTheBlackWidowP-61.pdf Pilot Training Manual for the P-61 Black Widow] | + | * [https://ia801208.us.archive.org/33/items/PilotTrainingManualForTheBlackWidowP61/PilotTrainingManualForTheBlackWidowP-61.pdf Pilot Training Manual for the P-61 Black Widow][[File:Pdf_fileicon.png|.pdf document|link=]] - By Headquarters Army Air Forces - Office of Flying Safety, 1944 |
| − | * [https://ww2aircraft.net/forum/threads/p-61-pilots-manual.6789/ Northrop P-61 Black Widow Pilot's Flight Operations Instructions] | + | * [https://ww2aircraft.net/forum/threads/p-61-pilots-manual.6789/ Northrop P-61 Black Widow Pilot's Flight Operations Instructions][[File:Pdf_fileicon.png|.pdf document|link=]] - Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions for Army Model P-61C Airplane, July 1945, ISBN:[https://www.google.com/search?tbm=bks&q=isbn:9781411689008 978-1-4116-8900-8] |
{{AirManufacturer Northrop}} | {{AirManufacturer Northrop}} | ||
{{USA twin-engine fighters}} | {{USA twin-engine fighters}} | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 21 February 2020
Contents
| This page is about the American twin-engine fighter P-61C-1. For the premium version, see P-61A-1. |
Description
The P-61C-1 is a rank American twin-engine fighter
with a battle rating of (AB), (RB), and (SB). It was introduced in Update 1.57 "Battle March".
The Northrop P-61C-1 Black Widow is a heavy twin-engine strike fighter designed as the USAAF's first dedicated night-fighter and aircraft outfitted with radar. Though a large aircraft with a crew of three (pilot, turret gunner and radio/radar operator/gunner), the Black Widow utilised its speed, radar, and weapons advantages to dispatch enemy aircraft in the dead of night.
The P-61C-1 is powered by dual Pratt & Whitney R-2800-73 double wasp engines, the same engines which powered the Republic P-47N Thunderbolt. The one difference between the Thunderbolt's -57C and the -73s built explicitly for the P-61 was each had a General Electric CH-5-A3 turbocharger installed. The modified engines allowed the P-61C-1 to fly at all altitudes effectively. While outfitted with powerful engines, turning the aircraft causes loss of energy, and such manoeuvres should be limited as places the aircraft in vulnerable situations.
One of the roles of the P-61C-1 is to operate as a bomber interceptor. During these operations, if detected, the heavy fighter is likely to encounter defensive fire. To increase survivability and protection of the crew, the Black Widow utilizes various bulletproof glass and armour protective plates throughout the fighter. The gunner who operates the remote turret has the option to utilise armour plates, which fold out of the way when not in use. The crew member sitting in the aft of the aircraft has the least amount of armour protection but is the least likely to be shot at unless being attacked from the rear.
The armament configuration of the P-61C-1 is unique compared to most fighters which either utilise nose-mounted or wing-mounted guns. The Black Widow incorporates two weapon systems, the first consisting of four 20 mm AN/M2 autocannons mounted in the belly of the aircraft with a total of 800 rounds of ammunition (200 RPG). Convergence is not a factor when utilising these guns. The aircraft also incorporates a dorsal turret outfitted with four 50 calibre machine guns (2,120 rounds or 530 RPG), which can be remotely operated by the gunner or the radio/radar operator. The turret has 360-degree mobility and can fire at elevations up to 90-degrees. The turret cannot depress lower than horizontal or else it would risk firing into the wings, cockpit, tail booms or tail section. The dorsal turret is utilised for both offensive and defensive uses.
General info
Flight performance
Describe how the aircraft behaves in the air. Speed, manoeuvrability, acceleration and allowable loads - these are the most important characteristics of the vehicle.
| Characteristics | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock | ||||||||||
| Max Speed (km/h at 7,100 m) |
Max altitude (meters) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (meters/second) |
Take-off run (meters) | ||||||
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||||
| 656 | 643 | 26.3 | 27.5 | 12.2 | 12.2 | 457 | ||||
| Upgraded | ||||||||||
| Max Speed (km/h at 7,100 m) |
Max altitude (meters) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (meters/second) |
Take-off run (meters) | ||||||
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||||
| 732 | 692 | 23.8 | 25.0 | 21.3 | 16 | 457 | ||||
- Takeoff and landing speeds (critical for Simulator battles)- all speeds in kph
- AB: 173 RB/SB: 163 - VR (aircraft rotate speed) - The speed at which the aircraft's control stick can safely be pulled back for takeoff, causing liftoff without risk of a tailstrike on the runway.
- AB: 126 RB/SB: 120 - VS0 - Landing speed with full flaps (depending on the aircraft, this could be landing flaps or take-off flaps).
- AB: 148 RB/SB: 145 - VS1 - Landing speed without flaps (clean). Knowing this speed is useful when the flaps are damaged or missing to prevent spins or tail strikes upon landing.
Details

| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X |
| Limits | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wing-break speed (km/h) |
Gear limit (km/h) |
Combat flaps (km/h) |
Max Static G | |
| + | - | |||
| 340 | ~7 | ~3 | ||
| Optimal velocities | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons (km/h) |
Rudder (km/h) |
Elevators (km/h) |
Radiator (km/h) |
| < 530 | < 420 | < 450 | > 337 |
| Compressor (RB/SB) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Setting 1 | ||
| Optimal altitude | 100% Engine power | WEP Engine power |
| 8,000 m | 2,200 hp | 2,783 hp |
Survivability and armour
- 12.7 mm Steel - Nose armour plating (behind radar unit)
- 60 mm Bulletproof glass - Pilot and gunner armoured windscreens
- 12.7 mm Steel - Gunner front armour (folds out of the way when not in use)
- 12.7 mm Steel - Lower gun plate
- 9.5 mm Steel - Gun turret ammo protection plates
- 12.7 mm Steel - Turret protection plate
With such beefy engines on the P-61C-1 it stood to reason that armour protection would be necessary to help protect the pilot and the gunner during a conflict against a potential bomber or attacker aircraft which may have defensive gunner positions. Since the main source of incoming bullets would most likely come towards the front of the P-61C-1 from defensive positions, it was reasonable to protect both the pilot and the gunner position, while the radio/radar operator received most of their protection from the gun turret and radio/radar equipment as there is no protection provided from the rear plane of the aircraft.
The pilot is afforded protection through the bulletproof canopy windscreen which is 60 mm thick and a 12.7 mm steel plate located directly behind the radar unit in the nose. These two items will aid to protect the pilot in the event a bomber or attacker’s defensive gunners fire on an attacking P-61C-1, however, note that these protections will wain in their ability if the pilot of the Black Widow decides to take another aircraft head-on, especially if that aircraft is sporting 20 or 30 mm autocannons.
The P-61C-1’s gunner sits directly behind the pilot, however, his station is slightly elevated giving him an unobstructed view of the front and side of the aircraft, allowing him great visibility to be able to aim and fire the machine gun turret. Since the gunner station is elevated, the gunner is exposed to incoming fire which the pilot's protective plate and armoured windscreen will not cover. To remediate this there are two 12.7 mm steel plates which the gunner can swing in front of him for protection or out of the way when not in use.
The rest of the armour protection for this aircraft are several steel plates which protect the critical components and the ammunition of the turret. Since the turret is mechanical in operation (remotely by the gunner or radio/radar operator), it is important that critical components are protected to ensure continued usage, as when the remote components fail, the turret is useless. Protecting the ammunition storage is also important not only to have it available for usage, setting the ammunition on fire or off in the storage container could cause catastrophic results to the aircraft and crew in the event they start firing.
Armaments
Offensive armament
The P-61C-1 is armed with:
- 4 x 20 mm AN/M2 cannons, belly-mounted (200 rpg = 800 total)
The P-61C-1 is armed with 4 x 20 mm AN/M2 autocannons which are mounted in the belly of the fuselage just below the cockpit. Each cannon is outfitted with 200 rounds which may not seem like very much, but for those who are conservative by maintaining trigger control (short bursts), the ammunition will go a long way. Having the guns clustered along the lower fuselage allows for both in-close and longer-ranged shots without the necessity of having to calculate for convergence, the only factor will be bullet-drop over a distance which comes with practice. The cannons are very effective when used against any aerial vehicle encountered as they have no problem disabling engines and destroying wings or puncturing fuel tanks.
Suspended armament
The P-61C-1 can be outfitted with the following ordnance:
- Without load
- 4 x 500 lb AN-M64A1 bombs (2,000 lb total)
- 4 x 1,000 lb AN-M65A1 bombs (4,000 lb total)
The P-61C-1 is typically used as a night or strike fighter which is used to sneak up on unwary targets and destroy them with the four forward-facing 20 mm autocannons, however, there is an opportunity to mix it up as a multi-role aircraft and outfit the plane with bombs. There are four external hardpoint pylons in which either 500 lb or 1,000 lb bombs can be loaded for a total of either 2,000 or 4,000 lbs of bombs. With payloads like this, the P-61C-1 can rival the B-25 bombers in their payload deliveries. Unfortunately, for a strike fighter, the P-61C-1’s flight performance and manoeuvrability suffer when adding the extra 2,000 or 4,000 lbs of weight and can be a challenge to fly when attacked, however after the bombs have been released on their target, the P-61C-1 can get back to its heavy-fighter role.
Defensive armament
The P-61C-1 is defended by:
- 4 x 12.7 mm Browning M2 machine guns, dorsal turret (560 rpg outer + 500 rpg inner = 2,120 total)
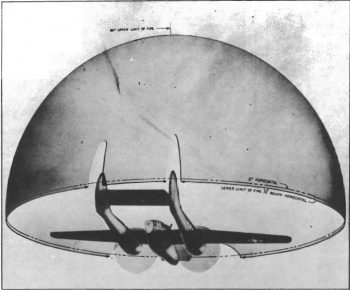
It is interesting to note that later fighters started to reduce or eliminate the ability to carry defensive weapons in order to help save on weight and crew needed to staff the aircraft, however, it was deemed necessary that the P-61C-1 should have a defensive turret. Utilising state-of-the-art technology, four .50 calibre machine guns were mounted on a dorsal turret which could be remotely controlled by either the gunner (sitting behind the pilot) or the radio/radar operator located in a separate compartment at the rear of the fuselage. The four machine guns in the dorsal turret had virtually a full 360° rotation field with an elevation straight up. Effectively the only dead zones for this turret were the upper propeller arcs and the vertical stabilizers to the rear. When enemy aircraft attempt to sit on the rear of the aircraft, the pilot will need to pitch the aircraft up and to one side or the other to allow the gunner the best possible chance of bearing the turret down on the enemy fighter.
Usage in battles
The below tactics are recommended for all game modes:
How to offensively engage an enemy aircraft: Climb to high altitude and keep on a straight heading once you have seen the enemy. Overshoot the enemy plane, then perform a 180-degree turn. Make sure you stay on his tail and gradually descend. It is recommended to do something similar to a shallow descent, where you can keep speed and height to your advantage in case the enemy aircraft changes course and altitude. Do not perform a dive which requires you to dive straight down since you will rip the wings off and crash. Once you are within firing range, fire a short salvo from your cannons. A couple of bursts from the Black Widow are sufficient to easily rip an enemy plane to shreds.
How to perform defensive fighting: When you are being engaged by an enemy fighter, make sure you keep descending. Very Important: Do not allow enemy aircraft to get lower than your elevator on the tail boom. You have no defensive armament to cover the belly or full-rear of the plane; these are your weakest defended parts.
- Tactic one: Descend slowly. Put the plane in a steep dive that does not exceed your structural limit. However, it must be steep enough to provide the turret gunner full visibility of the enemy plane. The four Browning machine guns will take care of the enemy plane.
- Tactic Two: Put the plane in a steep climb and make sure you set the throttle to at least 70%. Jump into the gunner turret and operate it. This will be the most accurate and fastest way of shooting down the hostile plane. When you operate the turret, make sure you try and perform defensive manoeuvres when operating it i.e. sharp turns, rapidly decreasing in height as well as gaining height and changing the speed of the plane in an irrational way. This will give you a higher chance of survival against the enemy.
Radars

The P-61C-1 is equipped with an AI Mk. X search radar, located in the nose of the aircraft. The radar utilised a 29 in (74 cm) parabolic dish which it rotated at 360 rpm when set to ranges below 100 miles, however, it is slowed down to 100 rpm when set to the 100 miles setting. The scopes could be set to one of four ranges, 1, 10, 20 or 100 miles (1.6, 16, 32 or 160 km). The parabolic dish could be adjusted to different altitude settings which included 0° to 0°, -5° to +5°, +5° to +20°, and +20° to +50°. One of the benefits to the multiple choices in range and altitude settings of the radar was that it provided partial immunity to chaff and other radar interference or countermeasures deployed by the enemy.
| AI Mk. X - Target Detection Radar | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Detection Range |
Guaranteed Detection Range |
Max Azimuth Scan Angle |
Max Elevation Scan Angle |
| 14,000 m | 8,500 m | ±75° | -20°/+40° |

Manual Engine Control
| MEC elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixer | Pitch | Radiator | Supercharger | Turbocharger | ||
| Oil | Water | Type | ||||
| Controllable | Controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Auto control available |
Controllable Auto control available |
Separate | Not controllable 1 gear |
Not controllable |
Modules
| Tier | Flight performance | Survivability | Weaponry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Fuselage repair | Radiator | Turret 12 mm | ||
| II | Compressor | Airframe | New 12 mm MGs (turret) | FMBC mk.1 | |
| III | Wings repair | Engine | Offensive 20 mm | ||
| IV | Engine injection | Cover | New 20 mm cannons | FLBC mk.1 | |
The P-61C-1 is a thoroughbred Boom & Zoom aircraft. However, when the plane is first unlocked the flight performance will be very lacklustre to support this tactic. As such, the initial priority should be to improve the aircraft, by researching the upgrades that improve flight performance the most, namely Compressor, Engine and Engine injection. When the flight performance has reached a satisfactory level to allow for effective Boom & Zoom tactics, the priority should be switched towards researching the New 20 mm cannons upgrade in order to improve the accuracy of the cannons. After this is done, either finish upgrading the flight performance or focus on the turret upgrade. The bomb racks should be left to research last, as they are not critical to the P-61's main role as a fighter.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- The offensive armament is mounted under the belly of the plane, this provides excellent accuracy
- Powerful offensive armament with 4 x AN/M2 cannons with a total amount of 800 rounds
- Powerful defensive armament with 4 x Browning machine guns in a rotating turret, a total of 2,120 rounds
- Defensive armament is able to be used offensively by the gunner
- Very stable climb rate
- Engines are able to cool down very fast
- Able to perform sharp movements at low and high speed
- Excellent bomber hunter
- Very strong and rugged airframe; is able to fly with wing tips missing
- Can keep a lot of momentum from a gradual dive
- Can carry 4 x 1,000 lb bombs: enough to fully destroy one base or four light pillboxes
- Air brakes installed, allows you to slow down faster for a bomb run or landing
- Powerful engines when upgraded giving great acceleration
- Can fly on one engine
- Fairly good roll rate at high speeds thanks to spoilers
- Very little adverse yaw effect thanks to spoilers (SB)
- Has access to a target detection radar, with much better range than German radars found around this battle rating
- Low stalling speed, enabling it to land on carriers
Cons:
- Slow acceleration when not upgraded and requires a long airstrip to take off due to weight
- Uncompetitive roll rate at slow speeds
- Bad turn rate (utilise Immelmann turns, chandelles or normal loops)
- Due to size, slow to gain speed in a dive, however, can exceed structural limits if not careful. Per the pilot's manual while in a dive:
- Between 0 - 10,000 ft do not exceed 415 mph IAS
- Between 10,000 - 20,000 ft do not exceed 375 mph IAS
- Between 20,000 - 30,000 ft do not exceed 305 mph IAS
- Bottom of aircraft is unprotected
- Large body airframe, not meant for turn-fighting (Boom & Zoom or Boom & Run)
- Dorsal turret might hit friendlies when active under AI control during furballs or when you're behind friendlies chasing an enemy
History
In 1940, the British Purchasing Commission wanted a high-altitude, high-speed interceptor to shoot down Luftwaffe bombers when they raided British cities. This called for a high-endurance heavy fighter with Aerial Interception (AI) radars and specified gun armament mounted in a 360 degrees gun turret. The requirements were sent to many aircraft manufacturers, one of them being Jack Northrop. The USAAC accepted his proposal, resulting in one of the most deadly and large fighters in World War Two. The prototype YP-61, had a long fuselage gondola in between two engine nacelles. The tail was a new radical twin-boom design. Full span flaps were fitted on the wings and it had two Pratt & Whitney R-2800-10 Double Wasp 18-cylinder radials, producing 2,000 horsepower each. The plane was mounted on a tricycle landing gear and had a three-man crew: a radar operator, gunner, and pilot. Armament includes four Browning 12.7 mm heavy machine guns mounted in a four-gun powered turret. The original design also had a ventral turret, but that was replaced by Hispano Mk.II cannons. Some versions also had air brakes so the pilot would not overshoot the target.
Media
- Images
- Videos
See also
External links
- Pilot Training Manual for the P-61 Black Widow
 - By Headquarters Army Air Forces - Office of Flying Safety, 1944
- By Headquarters Army Air Forces - Office of Flying Safety, 1944 - Northrop P-61 Black Widow Pilot's Flight Operations Instructions
 - Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions for Army Model P-61C Airplane, July 1945, ISBN:978-1-4116-8900-8
- Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions for Army Model P-61C Airplane, July 1945, ISBN:978-1-4116-8900-8
| Northrop Corporation | |
|---|---|
| Fighters | P-61A-11 · P-61C-1 |
| Jet fighters | F-89B · F-89D |
| F-5A · F-5C · F-5E | |
| F-20A | |
| Export | ␗F-5A · ▄F-5E FCU |
| USA twin-engine fighters | |
|---|---|
| P-38 | XP-38G · P-38E · P-38G-1 · P-38J-15 · Bong's P-38J-15 · P-38L-5-LO · P-38K · YP-38 |
| P-61 | P-61A-11 · P-61C-1 |
| F7F | F7F-1 · F7F-3 |
| Other | XF5F · XP-50 · F-82E |